Coalesce - AWS Fundamentals Workshop
Getting Started
- AWS Console Navigation Overview
- Intro to Root user vs IAM users
- Secure Root user - add MFA
- Intro to IAM Identity Center, Control Tower, and Organizations
- See this blog entry for overview
- Create IAM Administrator
- Grant IAM access to billing details
- Log in with IAM Administrator
- Budget Alarms
- Bills and Cost Explorer
- Intro to Regions and Availability Zones
- Choose your Region
- Static Website Demonstration
- Register Domain
- Transfer Domain
- Create ACM Certificate
- Create S3 Bucket and copy content
- Create CloudFront
- Update Route53 DNS Entries for CloudFront
- Review Workshop Website content
- Subscribe to Adobe ColdFusion 2023 on AWS Marketplace
- Enable CloudTrail and send trail to CloudWatch Logs
- Intro to AWS Systems Manager
IaaS
- Delete the default VPC
- Create new VPC - assign CIDR
- Review CIDR concepts
- Create Subnets
- Discuss public vs private subnets
- Review AZ's
- Create public
- Create private
- Create Gateways
- Internet Gateway
- NAT Gateways
- Create and associate Routes
- Security groups
- Define your Security Group goals
- Design Security Groups with as many references as possible
- Create primary security groups
- i. Load Balancer
- VPN Client
- CF Application Server
- Database Server
- Create IAM Instance Role
- Create Key Pair
- Launch EC2 Instance (CF Application Server)
- Launch RDS Instance (Database Server)
- Create Load Balancer Target Group
- Create Application Load Balancer
- Configure the DNS for ALB
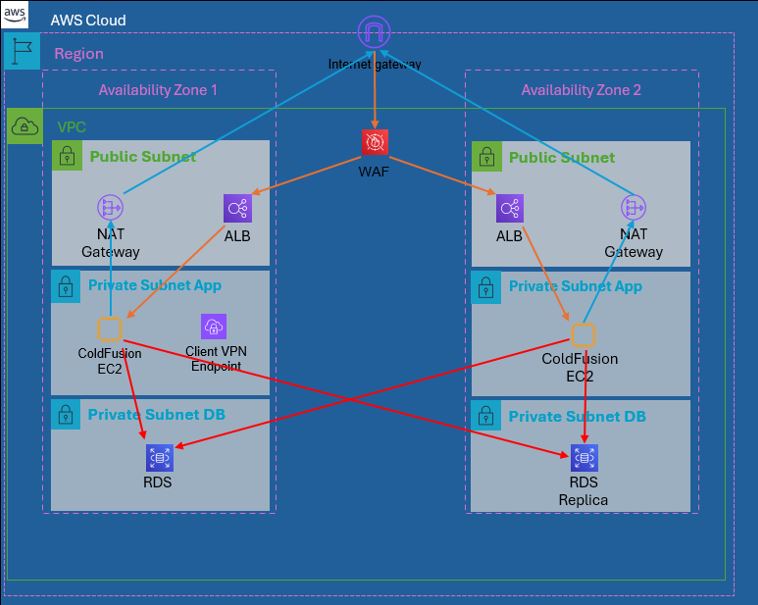
- Review Final Network Diagram
Administration
- Quotas
- SSM Connection Demonstration
- AWS Config
- GuardDuty
- Detective
- CloudWatch
- Security Hub
Create VPN (prereq - IAM Identity Center)
- Prep VPN Authentication in IAM Identity Center
- Add IAM Identity Provider
- Client VPN Endpoint
- Associate VPN with the Network
- Install AWS VPN Client and test
Advanced topics:
- Amazon Inspector - Scan your EC2 instances for vulnerabilities and compliance configurations
- DHCP Option Sets - private DNS resolution
- VPC Peering Connections - inter-account or inter-VPC network traffic
- VPC Flow Logs - network packet logging
- Database Parameters - Customize MySQL server settings, e.g. enabling lower-case table name
- Transit Gateways - useful for cross-region and more complicated structure network traffic
- VPC Endpoint Services (your services) - extend your services to other accounts/customers without traversing the internet
- VPC Endpoints (AWS services) - access AWS services without traversing the internet
- AMI's - Images of your EC2 instances
- Autoscaling Group - Creating a cluster of servers of the same image
- ElastiCache - Managed Redis service for caching and/or session storage
- SES - Simple email service
- Savings Plan and Reservations - save money and guarantee resource availability
- Trusted Advisor - Advisements on configuration, budgeting, and right-sizing. Requires business support for most features.
- Well-Architected Tool - Review your workloads against AWS best practices
- CloudFormation - Codify your IAAS
- EventBridge - Scheduled jobs
- IAM Identity Center - Central IAM access
- Organizations - Multiple AWS Account configurations and consolidated billing
- Control Tower - When using an Organization, using Control Tower on the management account lets you automate applying changes and policies for multiple accounts
- CloudWatch Log Agent - Accumulating CF logs off of servers into AWS Console
- AWS Support Tiers - AWS has multiple tiers of support available
Getting Started
Here is a quick view of the AWS services we will be covering today. At the end of this workshop, you will have some perspective of what these tools can do and will understand how easy it is to get started with each of them.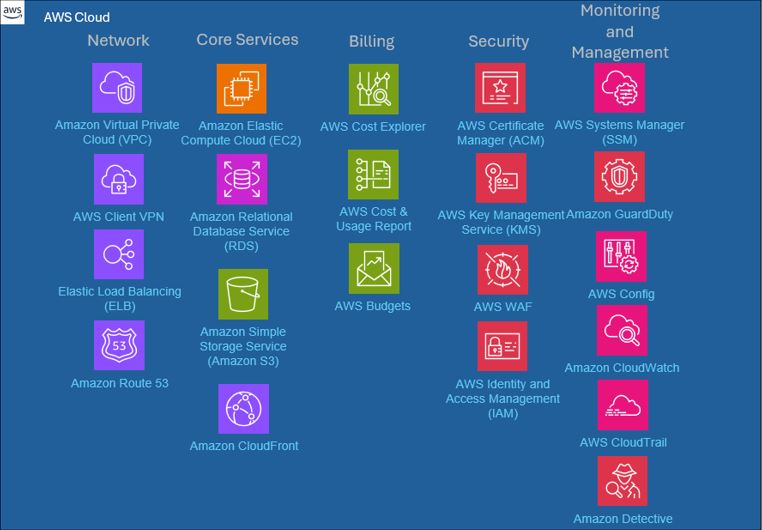
Price Estimator
Here is an estimator put together with some guesses at usage so you can understand the costs of deploying this guide.
https://calculator.aws/#/estimate?id=90879c8c3537795dae500a0ad1177758e01ae1f1
Note, this does not include the AWS Marketplace fees for licensing ColdFusion. The ColdFusion license will equate to approximately $360 per server and you will only pay for it while the server is running.
Identity and Access
- Intro to Root user vs IAM Users
Root users log in with email addresses, IAM users log in with account number and usernames.
Root accounts should only be used during initial setup, signup of support services, and emergency situations. - Add MFA To Root
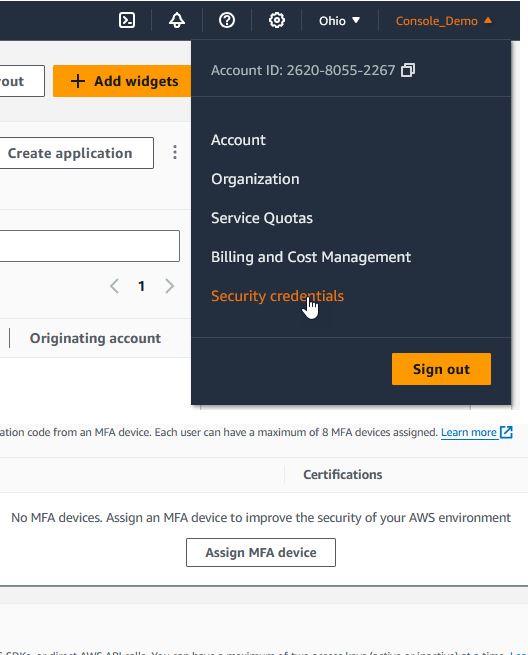
On your root user My security credentials page, under Multi-factor authentication (MFA), choose Assign MFA device.
On the MFA device name page, enter a Device name, choose Passkey or Security Key, and then choose Next.
On Set up device, set up your passkey. Create a passkey with biometric data like your face or fingerprint, with a device pin, or by inserting the FIDO security key into your computer's USB port and tapping it.
Follow the instructions on your browser to choose a passkey provider or where you want to store your passkey to use across your devices.
Choose Continue. - Intro to IAM Identity Center, Control Tower, and Organizations
- See this blog entry for overview
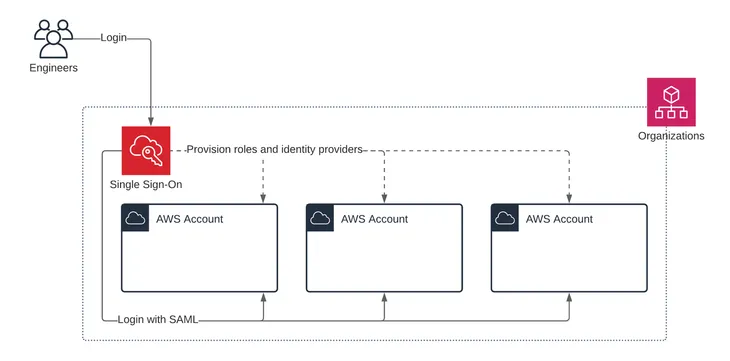
We are skipping creation of Identity Center since that requires an Organization to be set up. However, without setting up the IAM Identity Center, you will not be able to configure the VPN service as documented in this workshop. - Create IAM Administrator
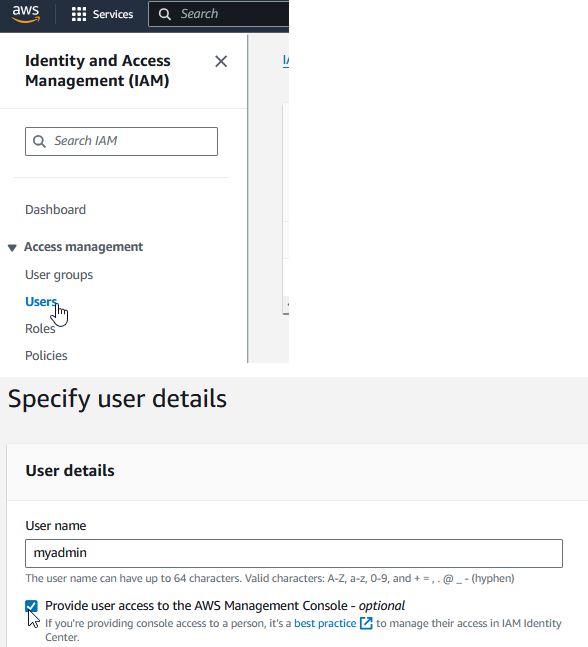
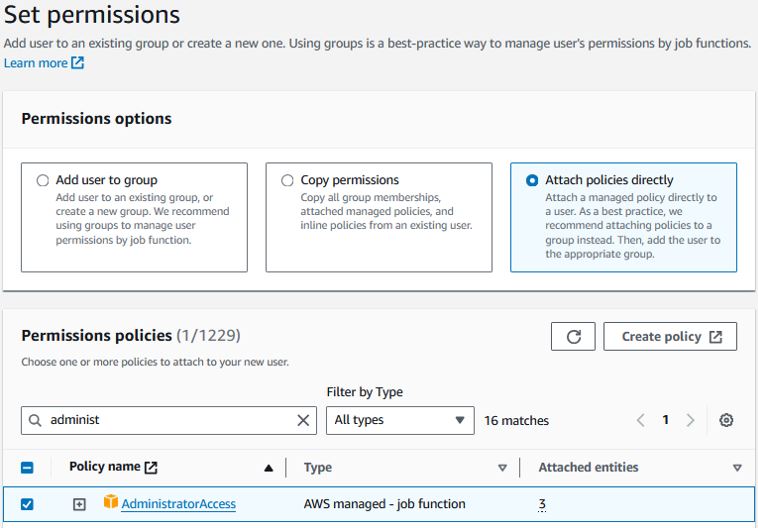
Go to IAM -> Users and add a user. Be sure to click the box to enable the user access to the AWS management console.
Attach IAM policy directly and select the AdministratorAccess policy. This will give full admin rights to this user. - Enable IAM to Access Billing
Before logging out of the Root account, be sure to allow IAM users access to the billing section of AWS.
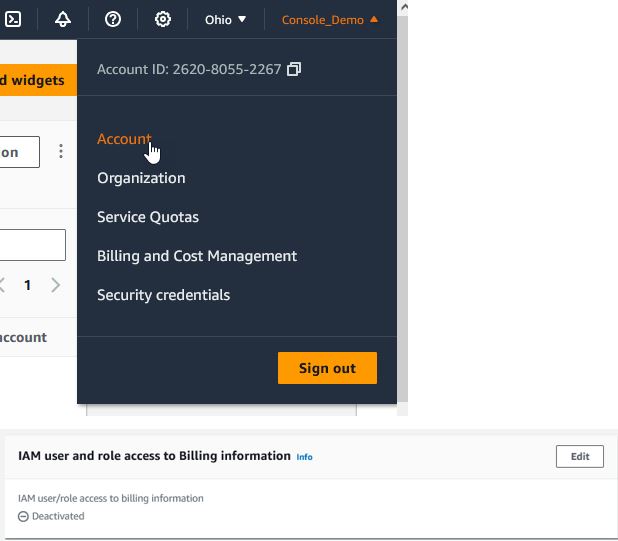
Click Edit by IAM user and role access to Billing information and enable the access.
- Log in with IAM Administrator
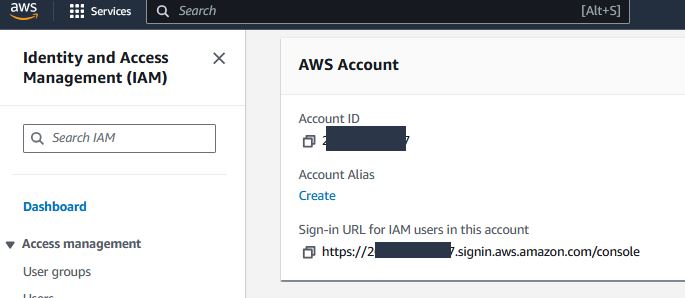
Within the IAM Dashboard, you will see a sign-in URL you can use to log in with your IAM user. Proceed to that URL and log in.
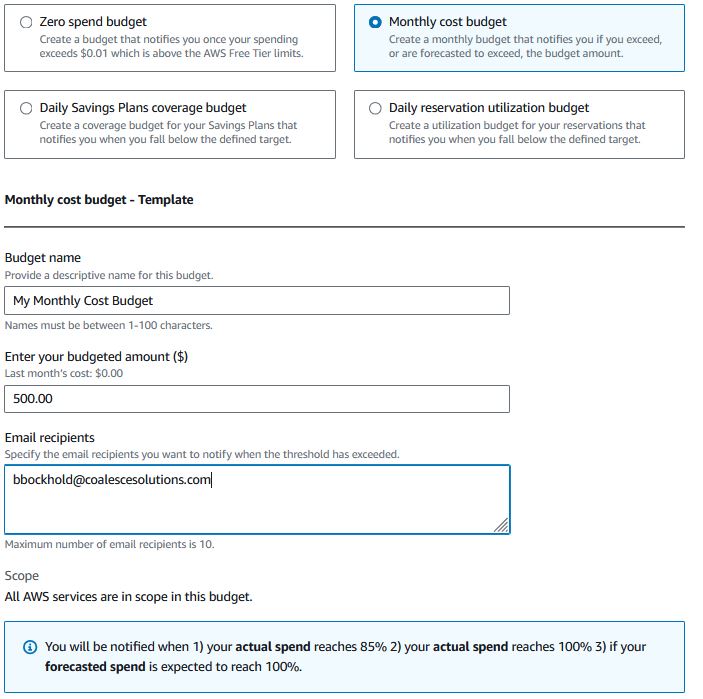
- Budget Alarms
Under Billing and Cost Management Budgets, click “Create budget”.
Select “Monthly cost budget”, give it a name you would recognize if you receive this alarm, set an amount for the trigger, and enter in your email addresses to send the alarm.
AWS will email you up to 3 times: if AWS determines you are trending higher than the defined amount, once you reach 85% of the alarm amount, and once you pass the alarm amount.
- Bills and Cost Explorer
Visit Billing and Cost Management and discuss viewing your Bills and Cost Explorer
- Introduction to Regions and Availability Zones
34 Regions, 108 Availability Zones
AWS has the concept of a Region, which is a physical location around the world where they cluster data centers. Each group of logical data centers are called an Availability Zone. Each AWS Region consists of a minimum of three, isolated, and physically separate AZs within a geographic area. Unlike other cloud providers, who often define a region as a single data center, the multiple AZ design of every AWS Region offers advantages for customers. Each AZ has independent power, cooling, and physical security and is connected via redundant, ultra-low-latency networks. AWS customers focused on high availability can design their applications to run in multiple AZs to achieve even greater fault-tolerance.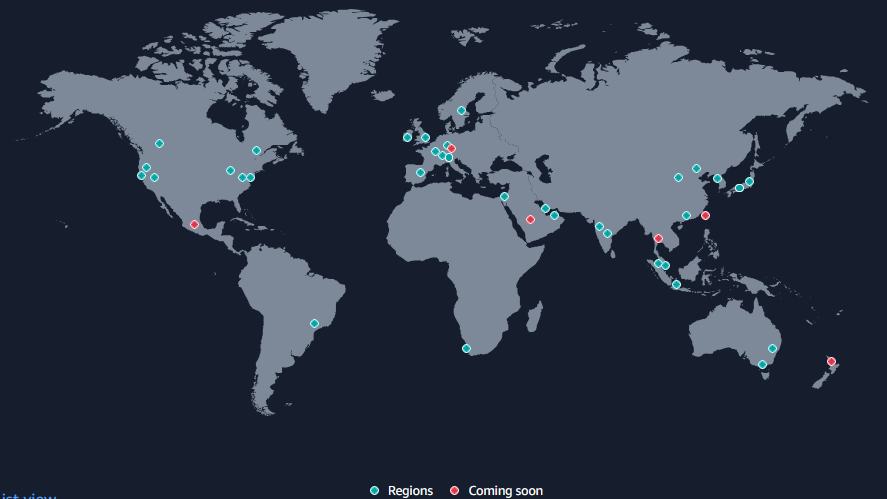

- Choose Region
The first major step when setting up your AWS account infrastructure, you need to select a region. Choose a region that works for your application.
Creating Workshop Static Website
In this example, we are:- Registering a new domain called cfquickstart.com in Route 53
- Creating a Certificate Manager (ACM) certificate to support HTTPS
- Creating an S3 bucket to store the website files
- Creating a CloudFront distribution for the website hosting and configuring it with the ACM certificate and S3 bucket.
- Updating Route 53 to point cfquickstart.com and www.cfquickstart.com to the new CloudFront distribution.
***Even though you may not have a static website to host, the Route 53 domain zone setup and Certificate Manager will be used later in the workshop.***
- Register Domain Name (Option 1)
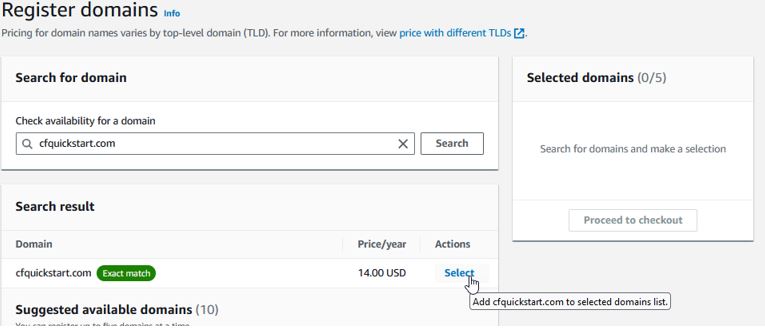
Select the domain name and checkout. Fill out the contact information and requisite questions and submit.
- Transfer Domain to AWS (Option 2)
Alternatively, if you already have a domain name and want to transfer it to Route 53, follow these steps.
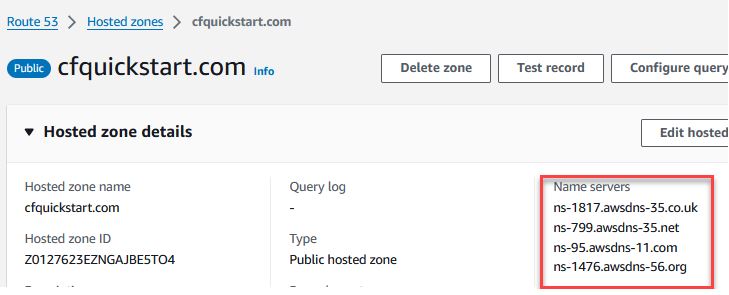
Create Hosted Zone in Route53.
After the Hosted Zone is created, take the Name servers given by AWS and update your registrar's (Godaddy, Network Solutions, etc) name servers accordingly. Please make sure to add your DNS records accordingly before transferring to AWS Route 53.
- Create ACM Certificate
Within Certificate Manager, select Request certificate.
Select public certificate and click Next.
Enter your domain name[s] (remember, *.cfquickstart.com will not work with the domain apex cfquickstart.com - so both will be needed to support apex and subdomains). Choose DNS Validation (what we're using) or Email validation; whichever you can use to validate ownership of the domain. Click Request.
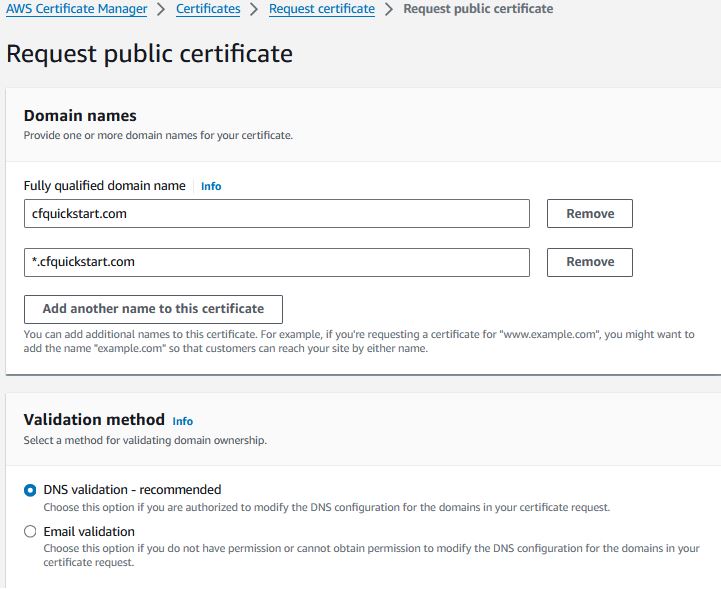
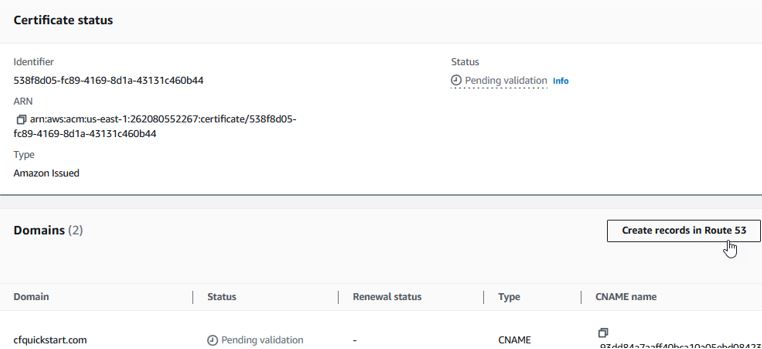
Once the Certificate is created, click the button “Create records in Route 53” and let it validate for you; or manually enter the provided CNAME[s] in your DNS zone.
Hosting static website on S3 and CloudFront getting started documentation:
https://docs.aws.amazon.com/AmazonCloudFront/latest/DeveloperGuide/GettingStarted.SimpleDistribution.html
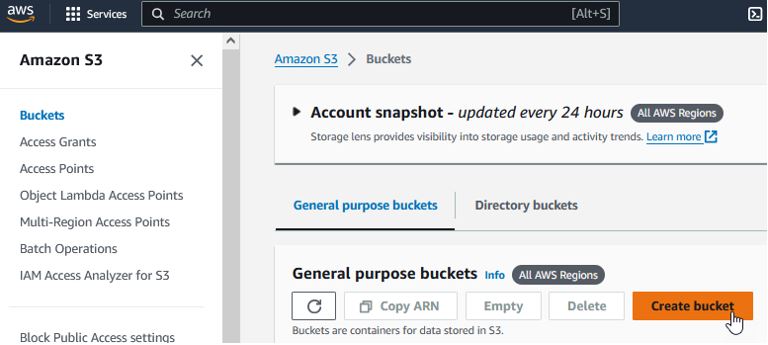
- Create S3 Bucket
Under Amazon S3, click "Create bucket" and come up with a unique name for your bucket and leave all other options default while creating
- Create CloudFront Distribution
During Creation:- Select your S3 bucket as the Origin domain
- Select Origin Access Control
- Create new OAC (accept defaults)
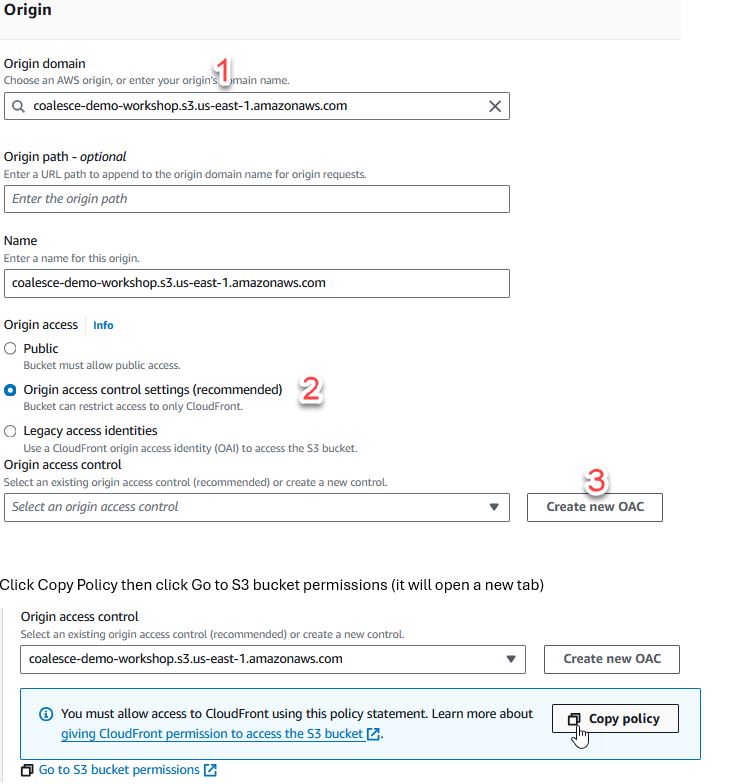
In the S3 Bucket settings, Permissions tab, Click Edit to edit the Bucket Policy. Paste the copied policy from the CloudFront distribution and click Save changes.
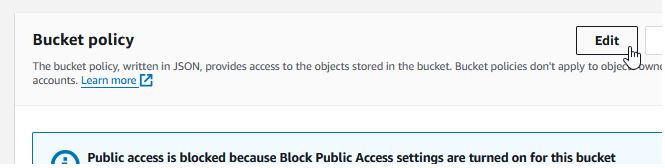
Return to the CloudFront browser tab and continue setting up the distribution.
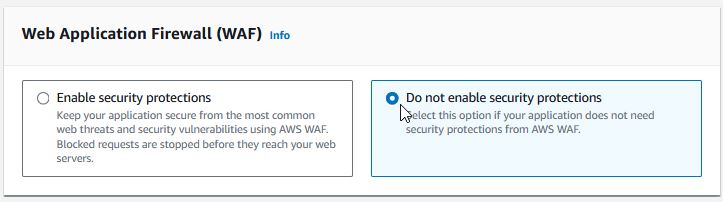
Choose to not enable WAF
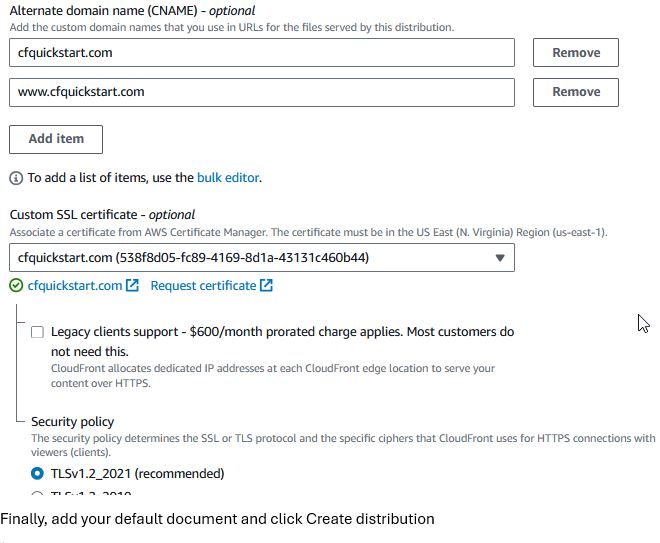
Further down the form, add your domain name(s) in the Alternate domain name (CNAME) and select your ACM certificate.
- Update Route 53 DNS entries to point website to the new CloudFront distribution
In Route 53 for the hosted zone, click Create record.
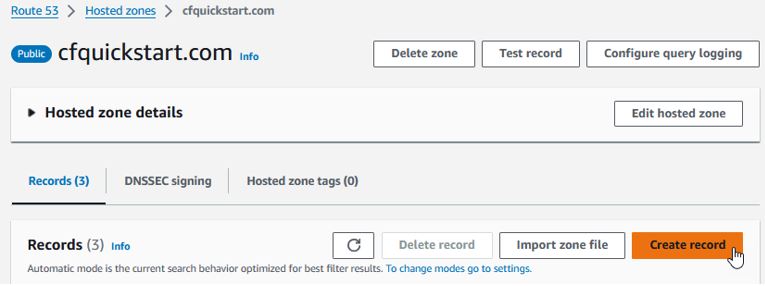
Switch the entry to use an Alias and leave the Record type as an A record.
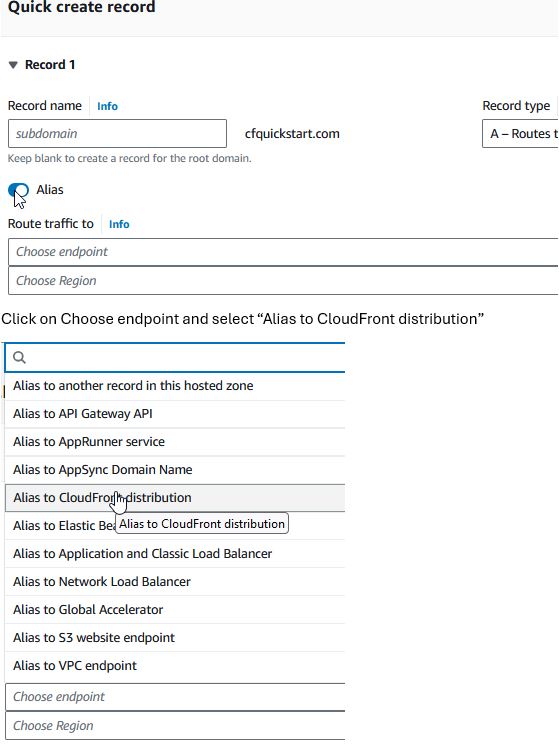
Click on Choose endpoint and select "Alias to CloudFront distribution"

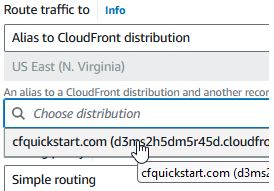
And select your CloudFront distribution.
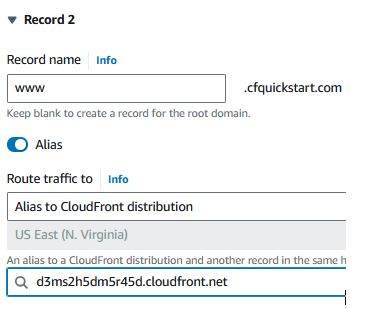
Click “Add another record” and repeat the steps for www.cfquickstart.com then click "Create records"
You're done! This has created a new static website on a new domain.
AWS Marketplace
Visit the Adobe ColdFusion 2023 Release listing - https://aws.amazon.com/marketplace/pp/prodview-ypcpaeaaxltu6Click "Continue to Subscribe"
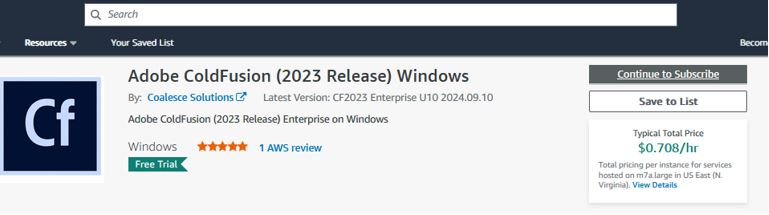
Then review the Terms and Conditions and click Accept Terms if it is acceptable to you.
This enables you to pay as you go for ColdFusion licensing.

CloudTrail
CloudTrail provides an audit log of every access or change within AWS - whether or it's in the AWS Console, CLI, or API call. Sending the CloudTrail logs to CloudWatch and S3 helps you maintain control of retaining this information.Visit AWS CloudTrail and click "Create a trail"
Give your trail a useful name and click "Create trail"
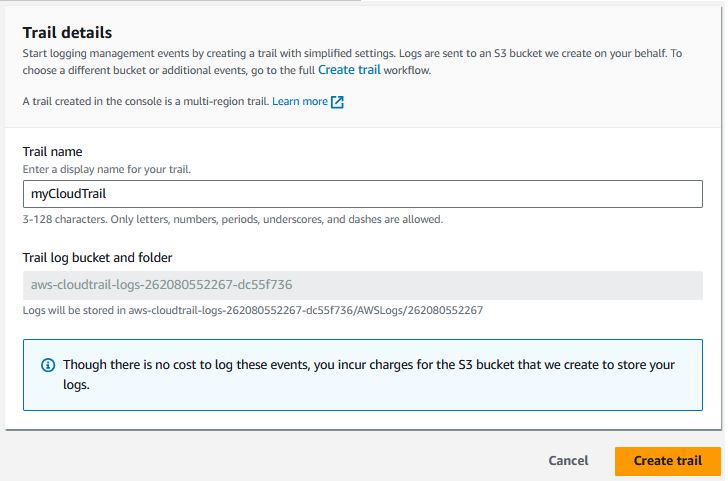
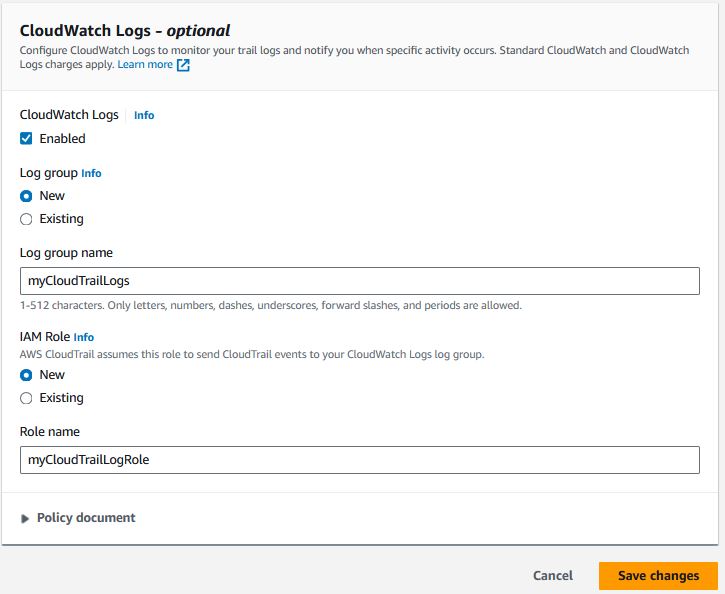
Click into your new trail and click "Edit" on the CloudWatch Logs section
Enable CloudWatch logs, create a new Log Group, and give the log group a useful name. Leave IAM role as New, give the role a useful name, and click "Save changes"
Session Manager Overview
- Remote connect (Session Manager) Quickly and securely access your Amazon EC2 instances through an interactive one-click browser-based shell or through the AWS CLI without the need to open inbound ports, maintain bastion hosts, or manage SSH keys.
- Resource grouping (Resource Groups) Make sense out of your AWS footprint by grouping your resources into applications.
- Running tasks on group resources (Automation) Use built-in automations or build your own to accomplish complex operational tasks at scale.
- Remote execution (Run Command) Safe and secure remote execution across instances at scale without SSH or PowerShell.
- Parameter store Centralized hierarchical store for managing secrets or plain-text data.
- OS patch management (Patch Manager) Simplify your operating system patching process for Windows and Linux.
VPC (Network) Setup
- Delete the default VPC
Under VPC, select the default VPC and select the Delete action and proceed to delete the VPC and included resources. - Choose your CIDR address range for your network
Use tools like www.subnet-calculator.com for help with ranges.
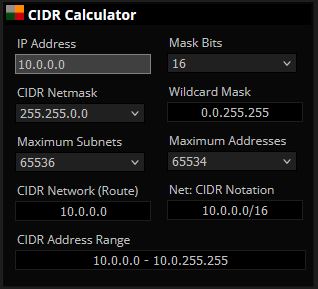
We will use 10.0.0.0/16 for the VPC network and will use 10.0.###.0/24 for each subnet.
10.0.0.0/16 is the range 10.0.0.0-10.0.255.255
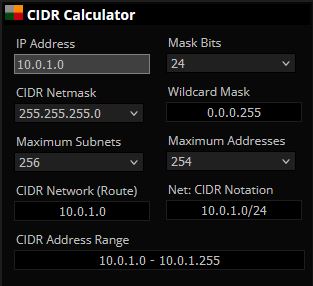
10.0.1.0/24 is the range 10.0.1.0-10.0.1.255
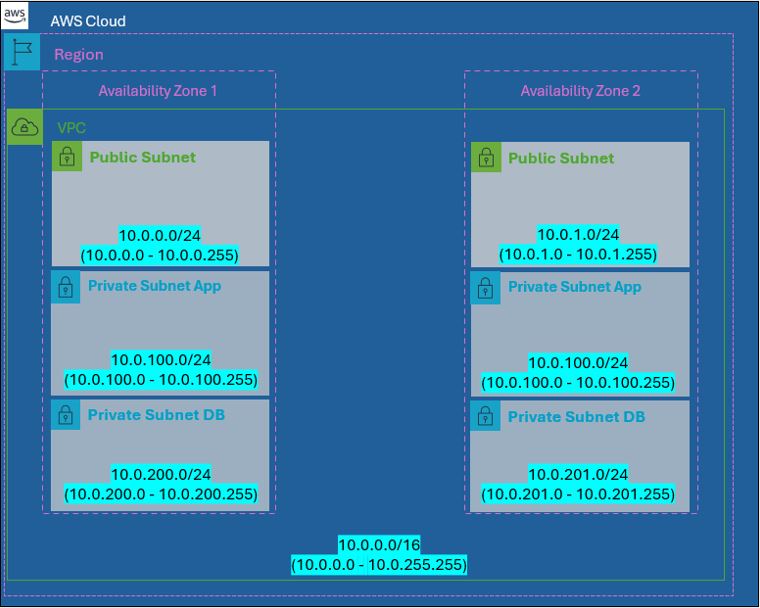
- Create the VPC
Here is the final goal for the VPC we will be creating; including the breakdown of AZ's, subnets, and CIDR's.
Under VPC, click Create VPC.
Select "VPC only" to be able to manually build every component. Optionally, you can use "VPC and more" to setup most of the network components in one step automatically.
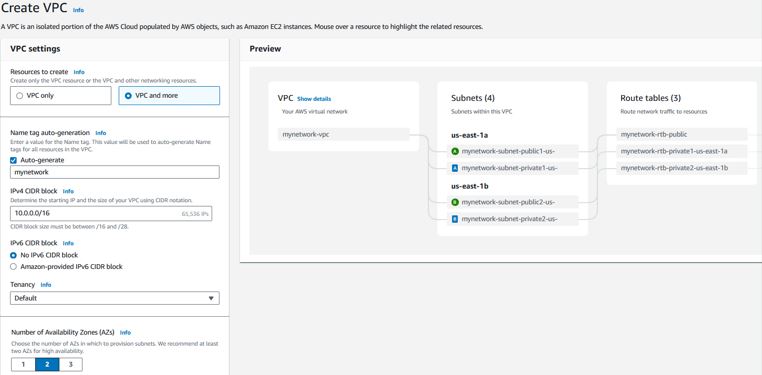
Submit the Create VPC form after inputting the VPC Name and CIDR
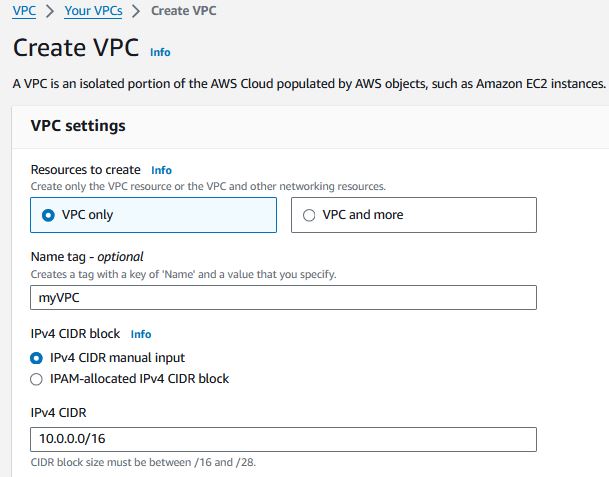
After VPC is created, edit the VPC settings and make sure the "DNS resolution" and "DNS hostnames" are enabled and click Save. Both of these are required for you to use RDS and other services.
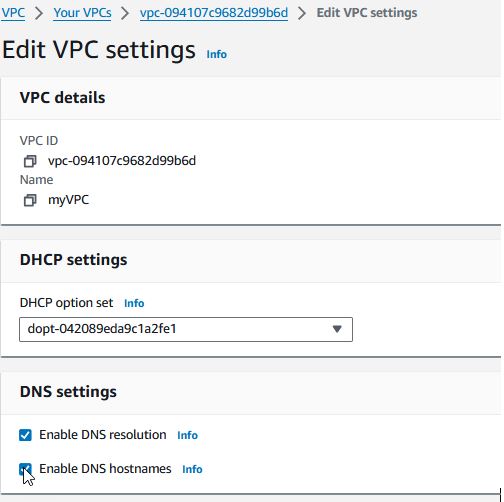
- Create the Subnets
Under VPC -> Subnets, click "Create subnet"
Select your VPC, give the Subnet a useful name (like "Public a" for the availability of the subnet and the AZ the subnet will reside), select an Availability Zone, and enter the subnet's CIDR block.
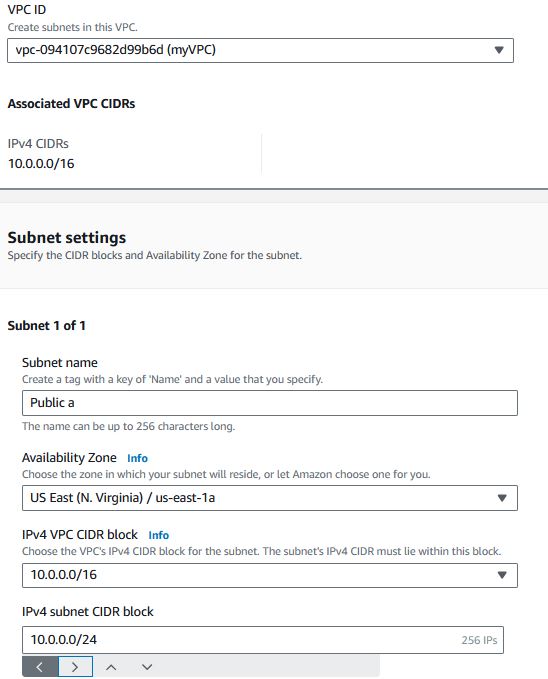
Repeat the settings for the rest of the Subnets:
Public b, us-east-1b, 10.0.1.0/24
Private App a, us-east-1a, 10.0.100.0/24
Private App b, us-east-1b, 10.0.101.0/24
Private DB a, us-east-1a, 10.0.200.0/24
Private DB b, us-east-1b, 10.0.201.0/24
In the end, it should look like this:
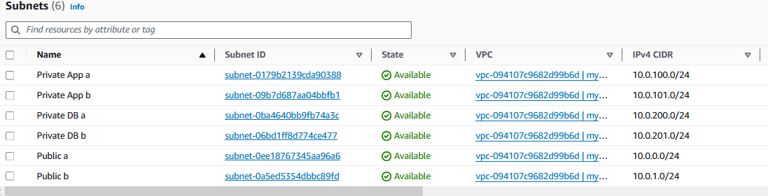
-
Internet Gateway
Under VPC -> Internet gateways, click "Create internet gateway"
Give it a name and click "Create internet gateway"
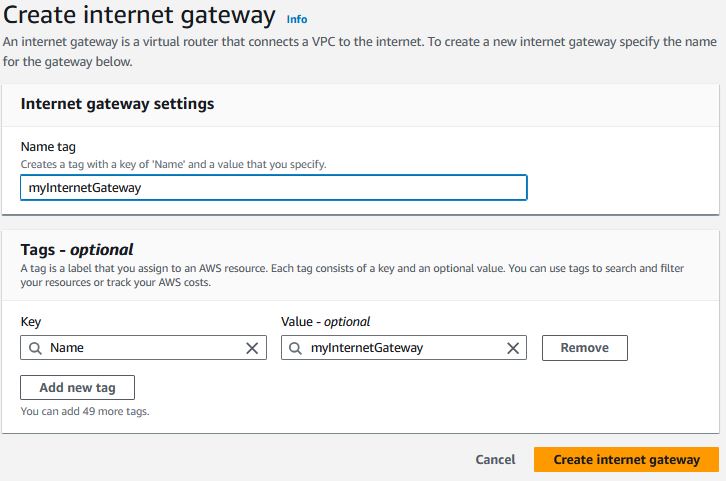
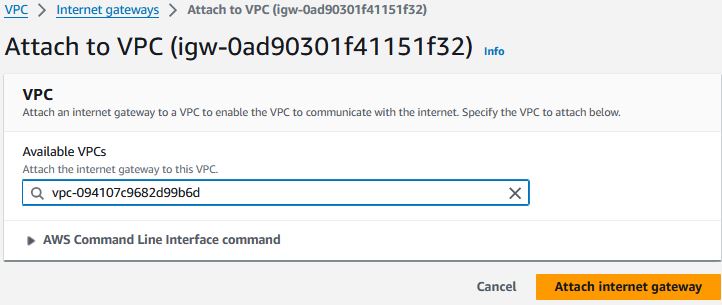
After the Internet Gateway is created, select the gateway and select Actions Attach to VPC
Select your VPC and click "Attach internet gateway"
-
NAT Gateways
We will be routing traffic based on the following diagram.
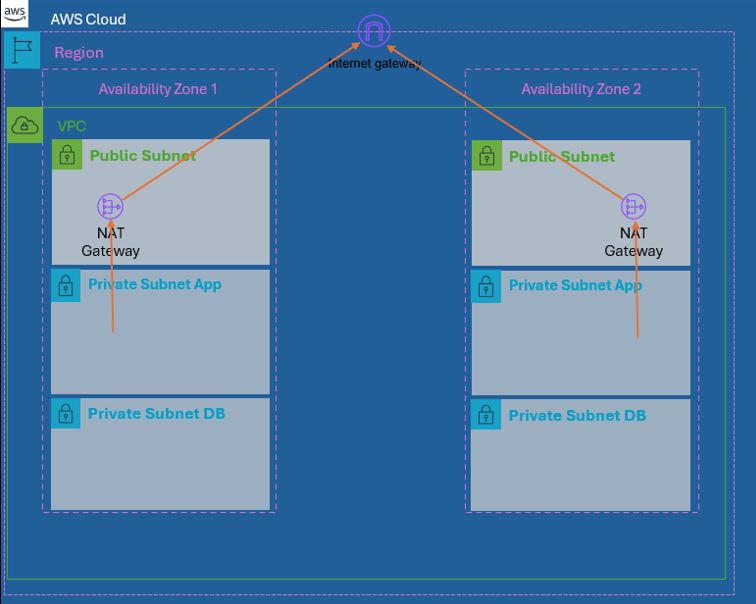
Under VPC -> NAT gateways, click “Create NAT gateway”
Give it a name (like “NAT a” with the “a” designating the AZ) and select your subnet in AZ a. Click on Allocate Elastic IP then click “Create NAT gateway”
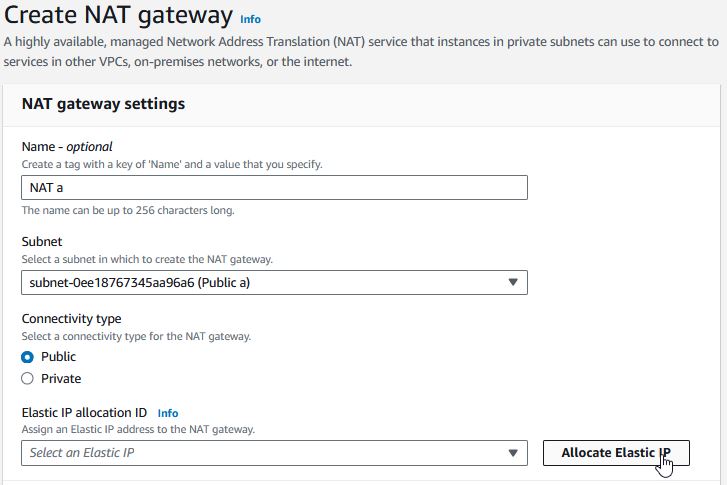
Repeat for the AZ b public subnet.
-
Network Routes
Under VPC -> Route tables, rename on the provided route table “Public Route”
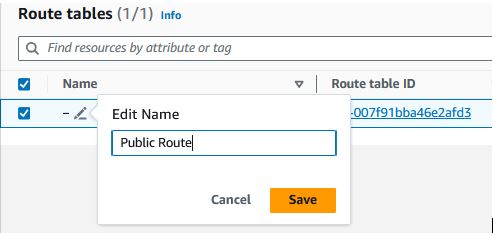
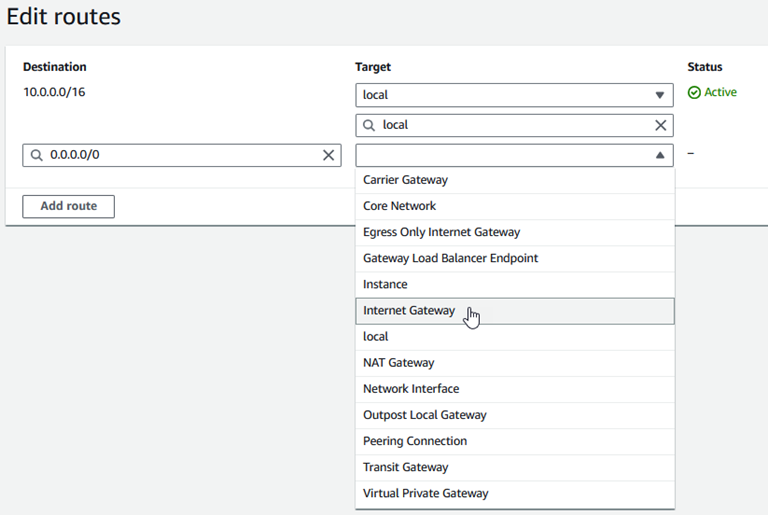
Edit the routes for the “Public Route”. Add a 0.0.0.0/0 destination route and target it to “Internet Gateway”
Select your Internet Gateway and click "Save Changes"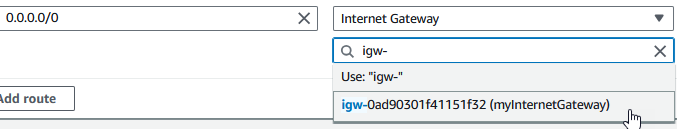
Create another Route Table called “Private NAT a”, Edit the routes, add a 0.0.0.0/0 destination route and target it to “NAT Gateway” and select your “NAT a” NAT Gateway and click Save.
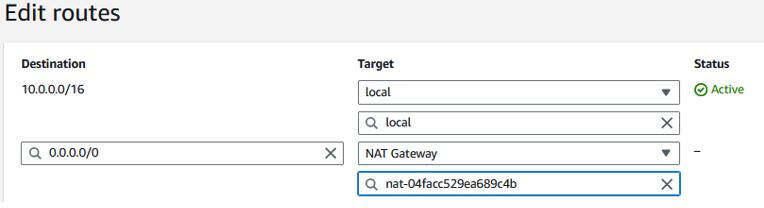
Repeat for “Private NAT b” with “NAT b”.
Create another Route Table for “Private Only” with no additional routes than the default local.
Click into “Private NAT a” and open the “Subnet associations” tab. Click “Edit subnet associations”, select “Private App a” and click “Save associations”.
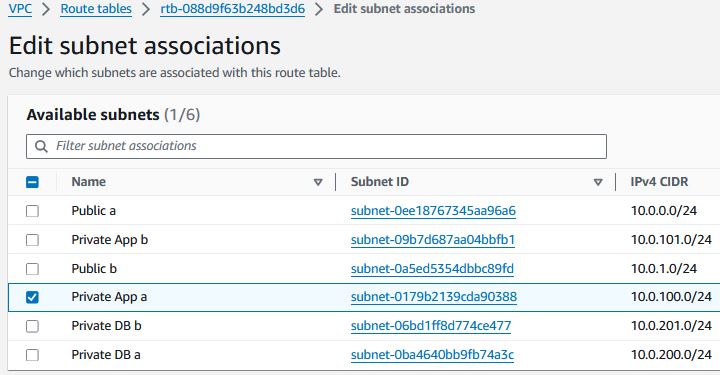
Repeat for “Private NAT b” with “Private App b”
Repeat for “Private Only” with “Private DB a” and “Private DB b”
Security Groups
-
Define your Security Group goals
Only allow network traffic that is required for your systems to operate.
-
Design Security Groups with as many references as possible
Security group rules can refer to other security groups by reference. Use this feature where possible.
-
Create primary security groups
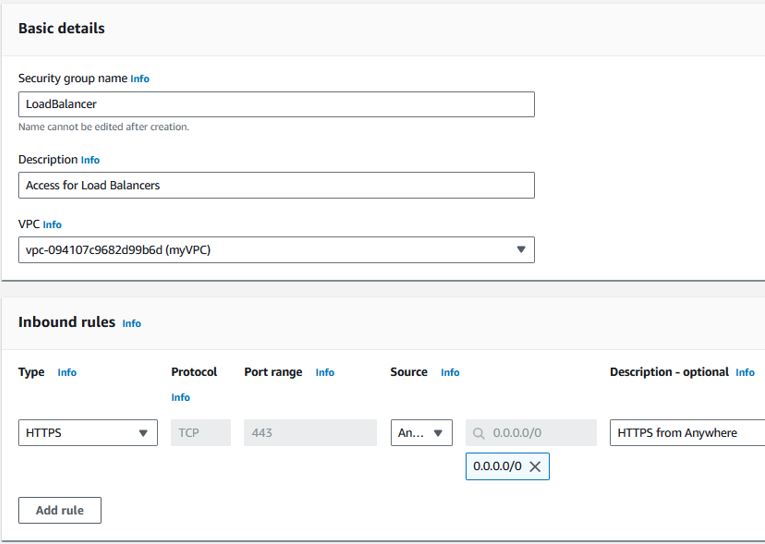
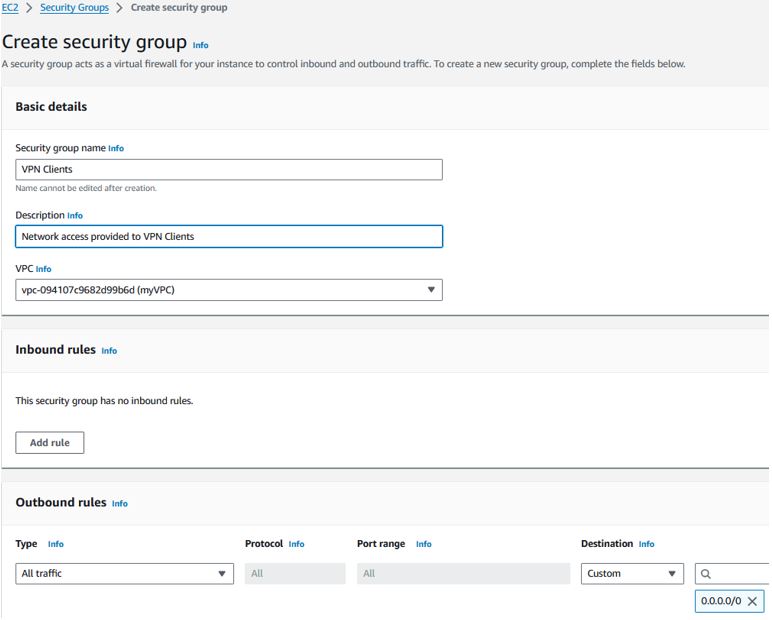
Under EC2 -> Security Groups, Click “Create security group”.
Add name, description, select your VPC, and define your inbound rules and click “Create security group” for each security group.
- Load Balancer
Inbound traffic from anywhere on HTTPS/port 443
- VPN Client
- CF Application Server
Allow inbound traffic from the LoadBalancer security group on HTTP/port 80. Start typing the LoadBalancer name in the “Source” field and select the associated security group.
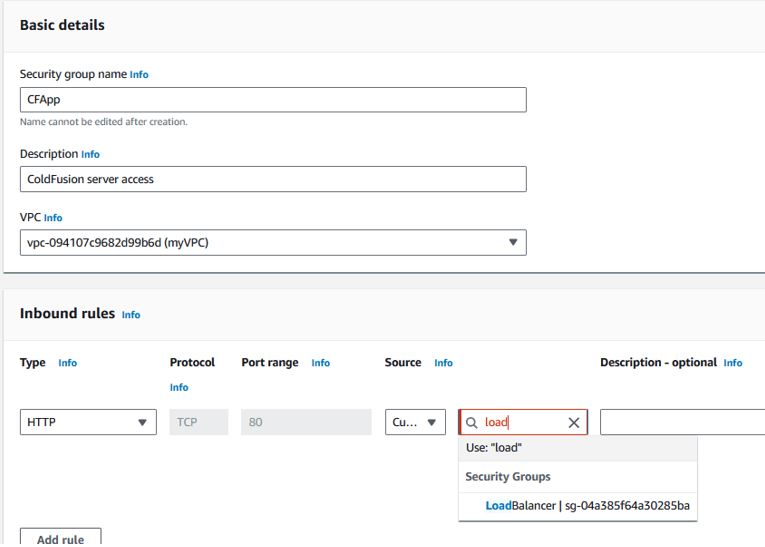
Add another inbound rule for TCP port 8500 from the VPN Clients security group. This will allow you to connect to the CF Admin while connected over VPN (assuming you permitted 10.255.*.* as a permitted connection within the CF Admin). Add any other ports you need to use while connected over VPN (RDP, SSH, HTTP, etc). - Database Server
Add two inbound rules for MySQL/Aurora, one for CFApp and another VPN Client. This will allow the CF App Servers and VPN connections the ability to connect to the database.
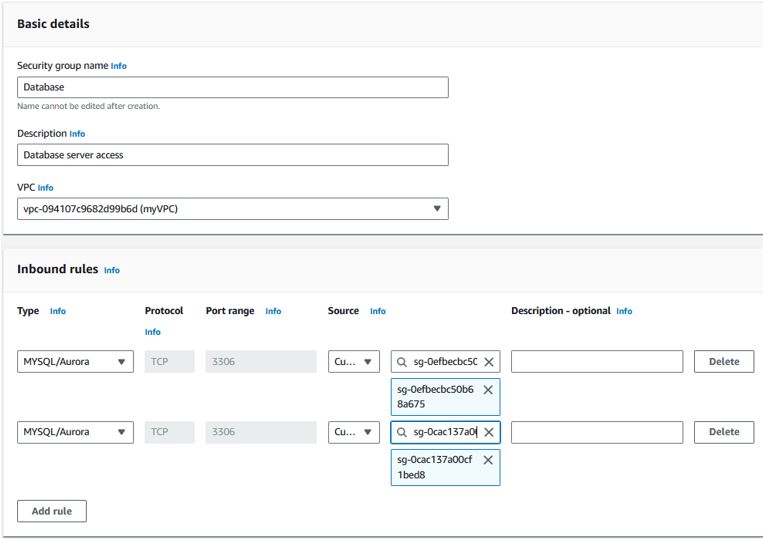
- Load Balancer
Create VPN
- Prep VPN Authentication in IAM Identity Center
Create Application in IAM Identity Center, following these instructions:
https://aws.amazon.com/blogs/security/authenticate-aws-client-vpn-users-with-aws-single-sign-on/
Complete the To create the VPN client SAML application section and do not proceed past To create the VPN client self-service SAML application:
It's buried in the instructions, but be sure to download the IAM Identity Center SAML metadata file during the Application creation process.
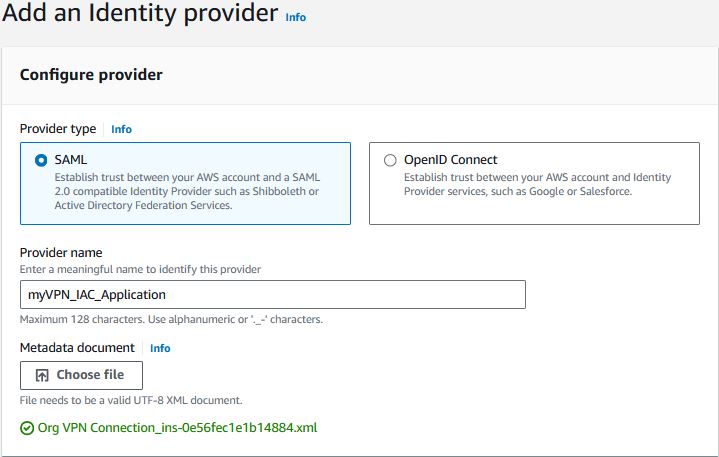
- Add IAM Identity Provider
In the AWS account that you are creating the Client VPN Endpoint, go to IAM -> Identity Providers and click “Add provider”
Give the provider a name and choose the SAML metadata file you downloaded in the previous step.
- Client VPN Endpoint
Under VPC -> Client VPN endpoints, click “Create client VPN endpoint”
Choose a Client IPv4 CIDR within the range of your VPC, but not used by one of your subnets. We are using 10.255.0.0/16
Choose Federated authentication and select the AWSSSO option you created earlier in the IAM IDP.
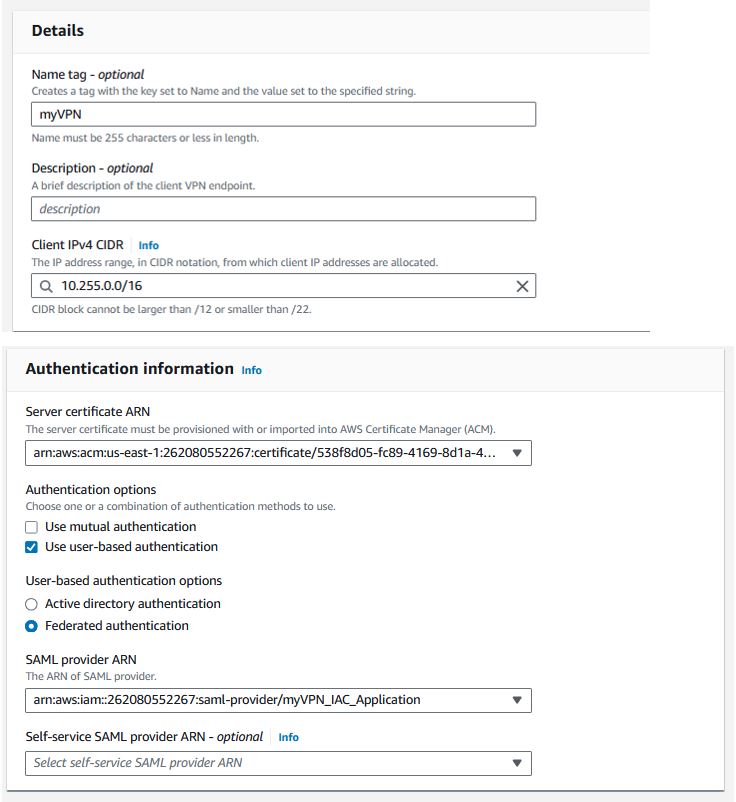
Enable split-tunnel if you don't want all user traffic to route through the client VPN endpoint.
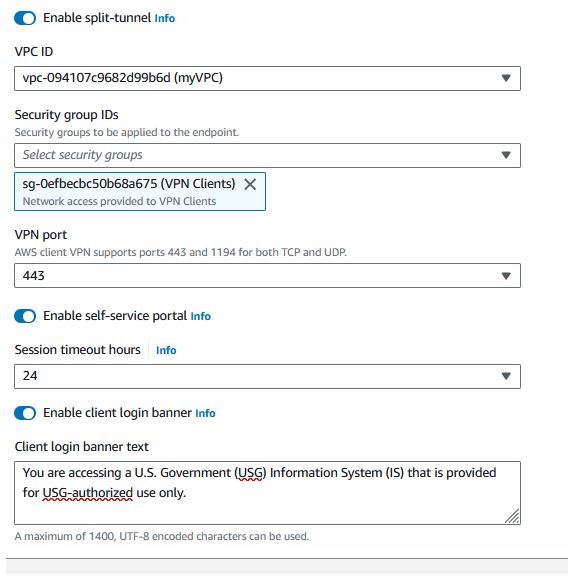
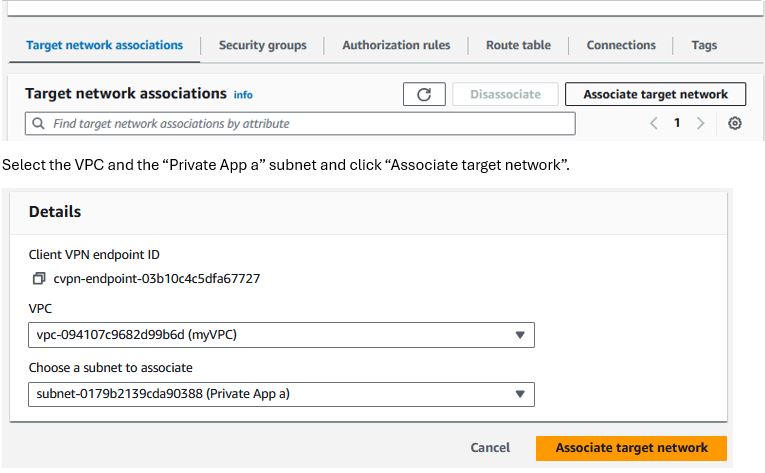
- Associate VPN Within the Network
In your new Client VPN Endpoint under the “Target network associations” tab, click “Associate target network”
- Setup Client
In your new Client VPN Endpoint, click on “Download client configuration”
- Install AWS VPN CLient
https://aws.amazon.com/vpn/client-vpn-download/
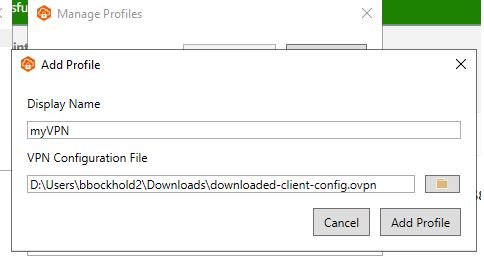
Open the AWS VPN Client application. Under File -> Manage Profiles, click “Add Profile”
Click the profile the name “myVPN” and select the VPN Client Configuration File you just downloaded.
Test VPN Connection
Select the VPN profile myVPN and click Connect. This will open your browser to the IAM Identity Center login page. If it does not open your browser and gets stuck in an endless Connect/Disconnect, then your Client VPN may be still associating with the network.
Create IAM Instance Role
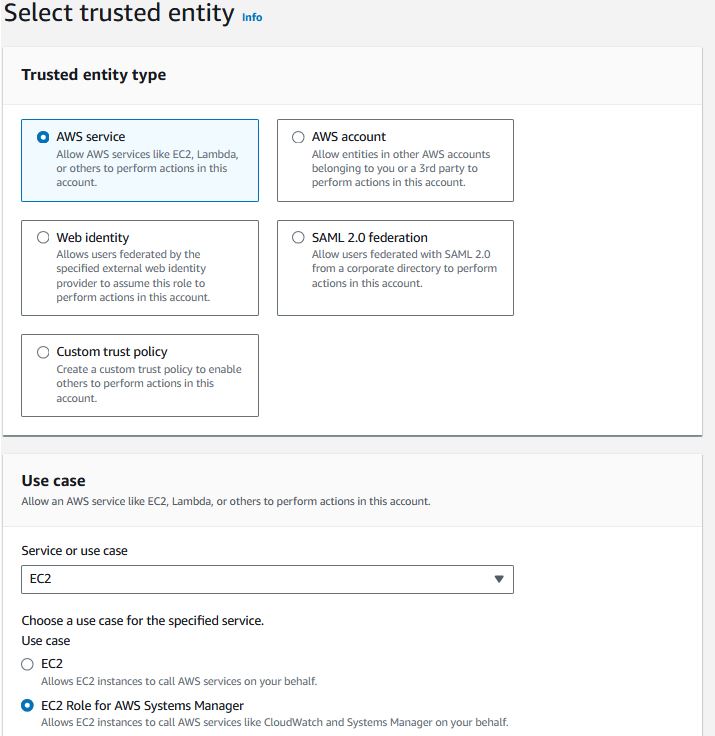
Your CF App Server needs AWS permissions to talk to AWS services for SSM connectivity, log reporting, etc. This permission is defined by the role you assign to the EC2 instance.Under IAM -> Roles, click “Create role”
Select “AWS service” trusted entity type and “EC2 Role for AWS Systems Manager” Use case, click “Next”, and “Next”. Give a useful name to the role like “CFAppRole” and click “Create role”.
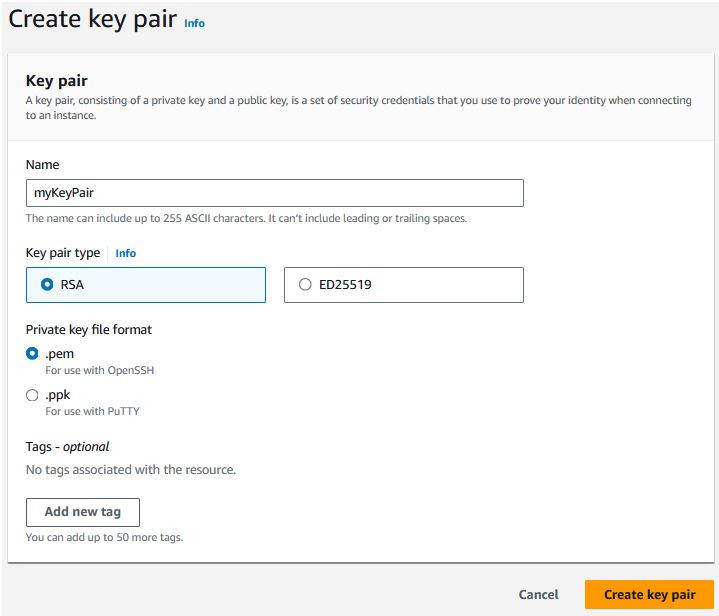
Create Keypair
Key Pairs are the security certificates that permit you to either access your servers or retrieve their passwords.Under EC2 -> Key Pairs, click “Create key pair” and give the key pair a name.
For Windows servers:
Select RSA as the type and choose .pem for the format.
For Linux servers:
Select RSA or ED25519 as the type (some newer Linux builds, such as Amazon Linux 2023, require ED25519 key pairs for SSH connectivity) and choose .pem or .ppk based on your needs (you can use tools to generate the other format).
Click “Create key pair”.
This will immediately download the key pair file. Keep this file in a safe place as you will use it later.
EC2 - The Servers
Launch EC2 Instance
Under AWS Marketplace -> Manage Subscriptions, click “Launch” on the Adobe ColdFusion (2023 Release) Windows.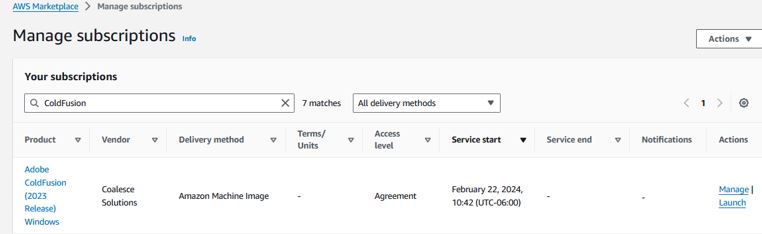
Make sure the region is correct and click “Continue to launch through EC2”
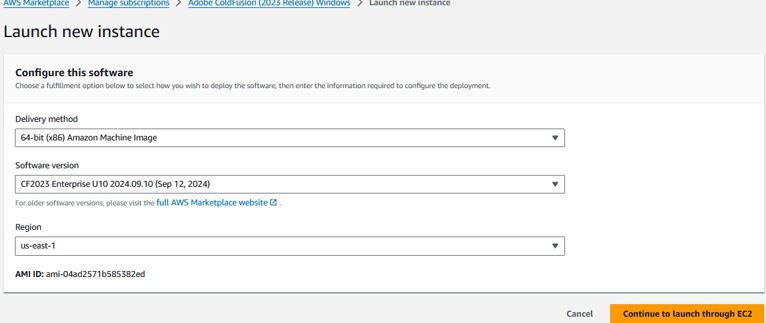
On the Launch an instance page, set the following:
-
Give the instance a useful name
-
If you want to stay under the AWS Free Tier, keep the Instance Type t2.micro. For the server to be usable, change the Instance Type to t3a.large. For a thorough breakdown of instance types and their prices, please visit https://instances.vantage.sh/
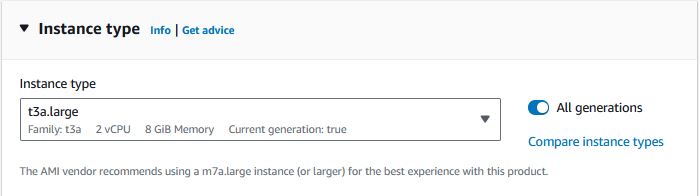
-
Choose the keypair you created earlier.
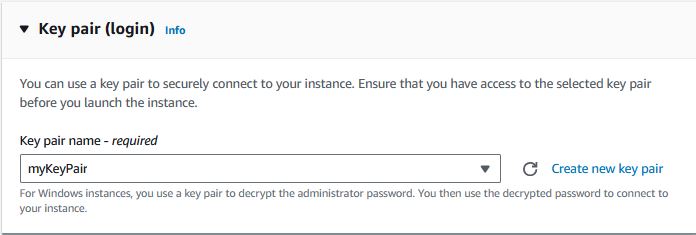
-
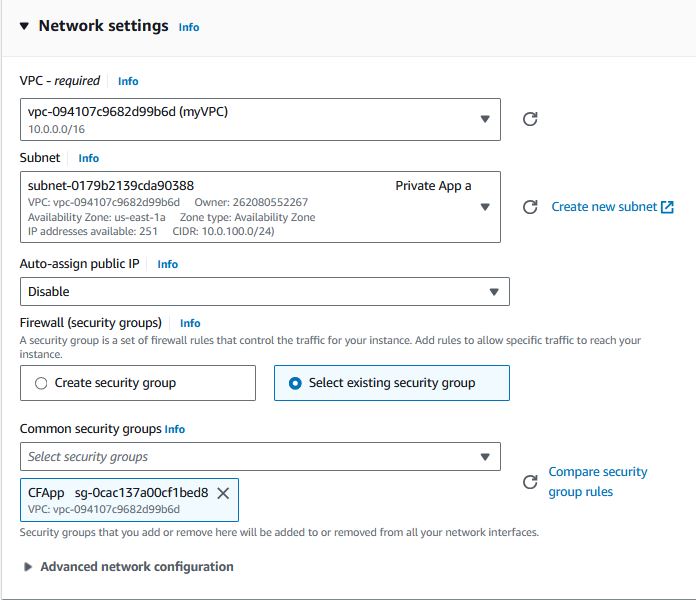
Click Edit on the Network settings section.
- Select Subnet “Private App a”
- Select existing security group CFApp
-
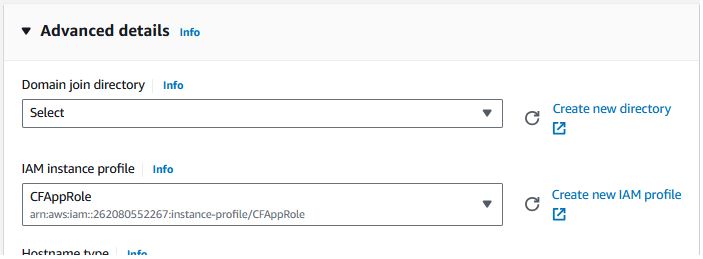
Under Advanced Details.
- Change the IAM instance profile to the IAM role we created earlier
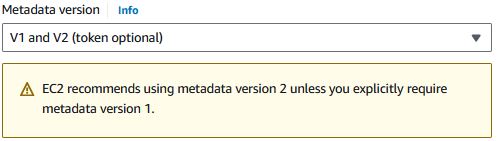
- Change the Metadata version to “V1 and V2 (token optional)”
- Change the IAM instance profile to the IAM role we created earlier
-
Click “Launch instance”
(Optional) Repeat for the second instance and place it in “Private App b”
RDS - The Database
Launch Database
-
Under RDS -> Subnet groups, click “Create DB subnet group”
Give it a useful name, choose your VPC, AZ's 1a and 1b, and select your private DB subnets (it's easiest to identify by IP CIDR). Click “Create”
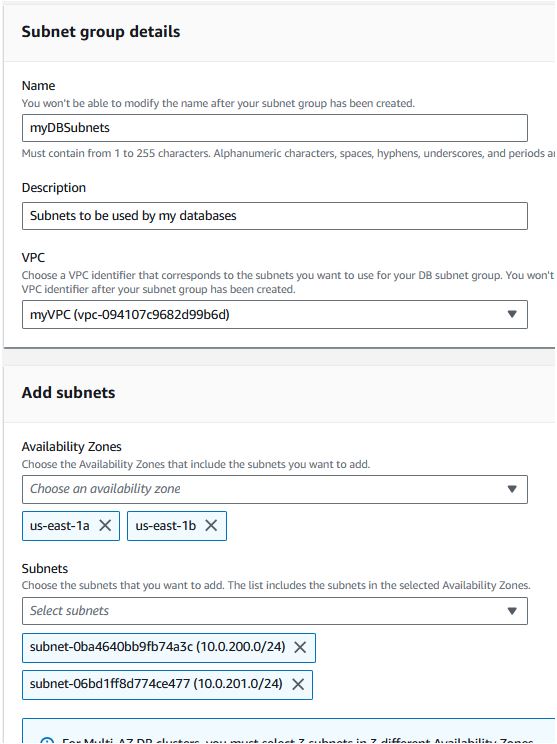
-
Under RDS click “Create database”
-
Select the Aurora MySQL engine type.
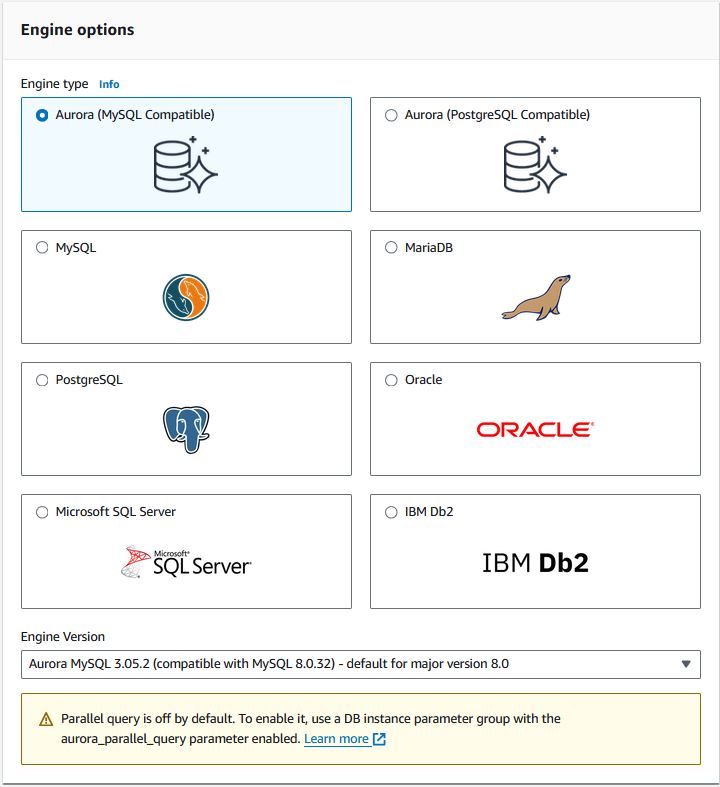
-
Name the DB Cluster, change the credentials to be “Self managed” and check the “Auto generate password”
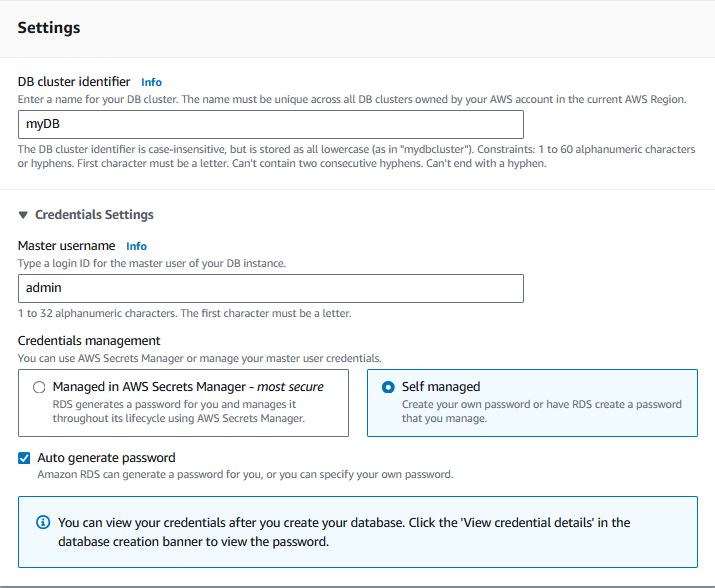
-
Choose burstable classes and select the t3.medium or t4g.medium type. Make sure an Aurora Replica will be created.
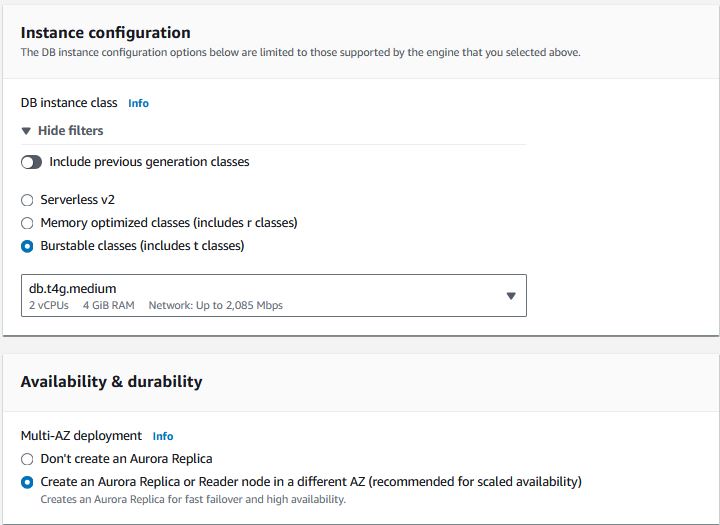
-
Select the DB Subnet group we created previously. Select “Choose existing” security group and select the Database security group we created previously.
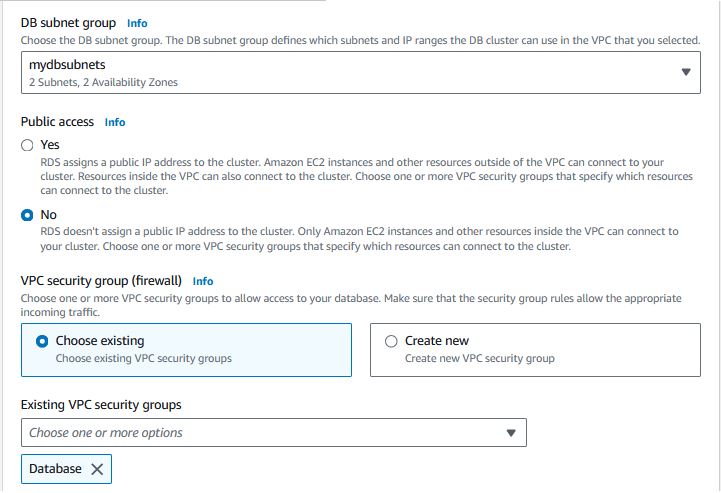
-
Uncheck the DevOps Guru and Enhanced Monitoring
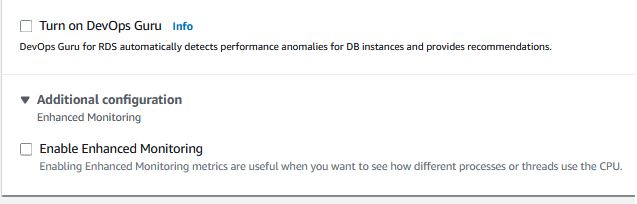
- Click “Create database”
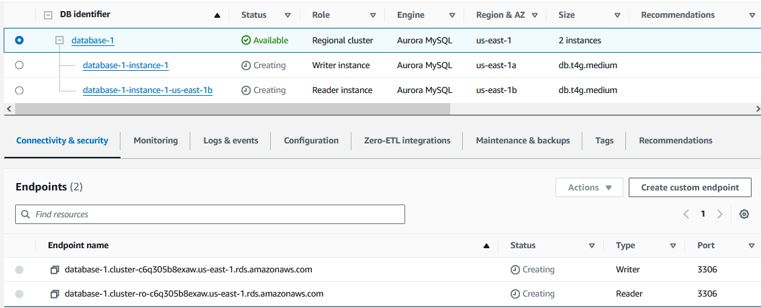
Deleting the RDS Cluster
When you are ready to delete the RDS cluster, you need to modify the cluster and disable “Deletion protection” and apply it immediately.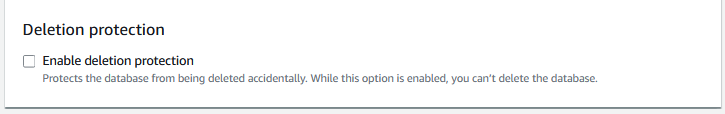 Once you do that, delete each individual instance. Once all instances are deleted, you can delete the cluster.
Once you do that, delete each individual instance. Once all instances are deleted, you can delete the cluster.
Load Balancer
Example components of the ALB
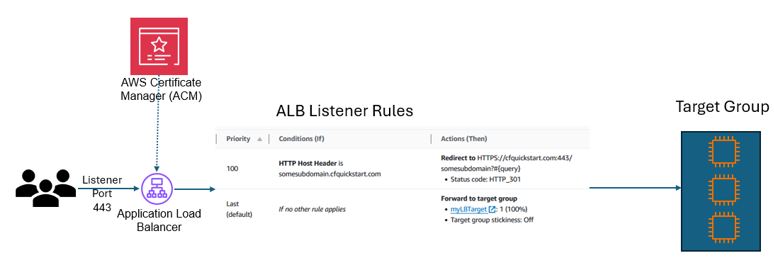
Create Target Group
Under EC2 -> Target Groups, click “Create target group”Choose the “Instances” type.
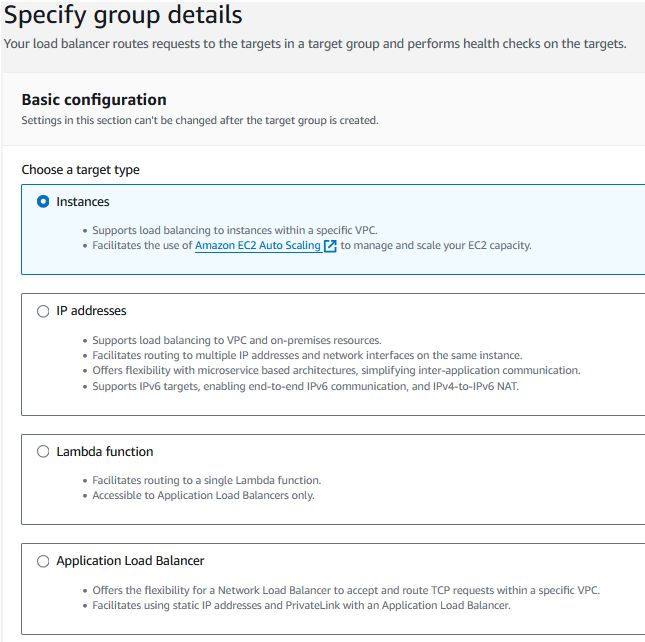
Give the Target group a useful name.
Protocol : Port should be HTTP 80 or HTTPS 443. This is the port in which your server is listening (regardless of how the end user will connect)
Choose a health check protocol and path that makes sense for your application. We'll leave it as HTTP and / respectively.
Click Next.
Check the instances you want to add to this Target Group and click “Include as pending below”.
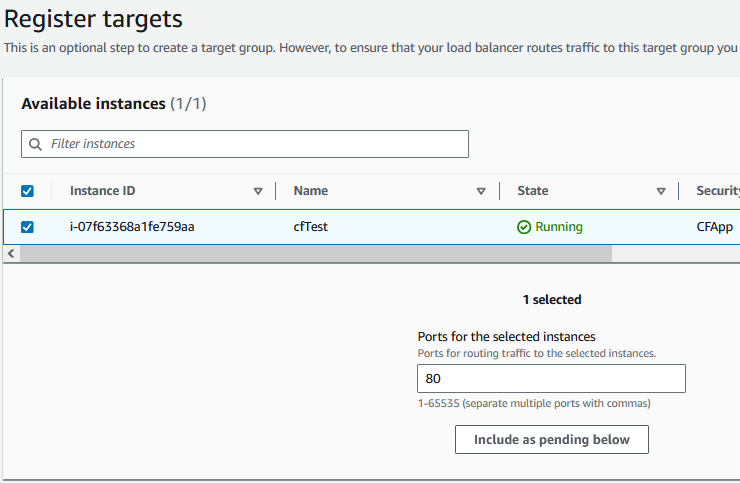
Click “Create target group”
Create ALB
Under EC2 -> Load Balancer, click “Create load balancer”Create an “Application Load Balancer”
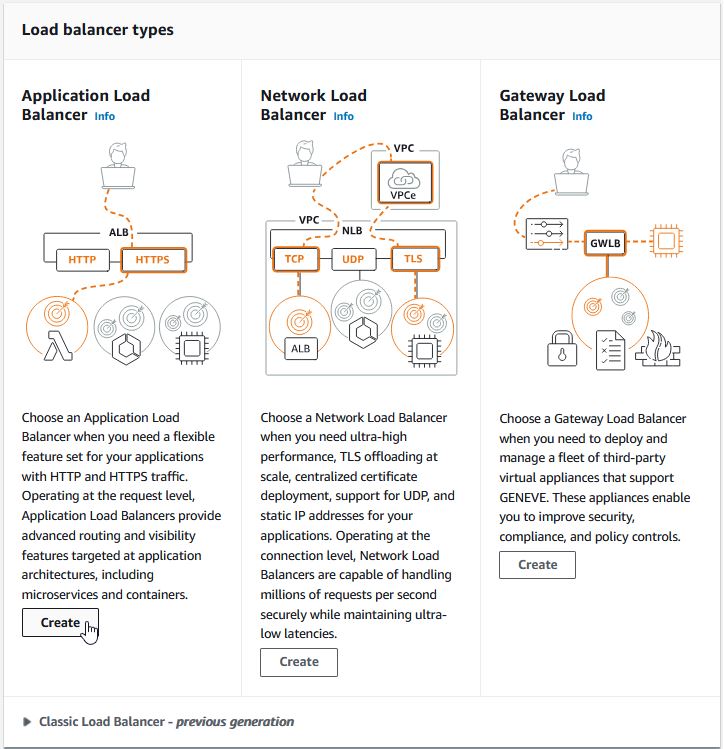
Give the Load Balancer a useful name.
Select your VPC and your AZ's and choose your Public subnets in each.
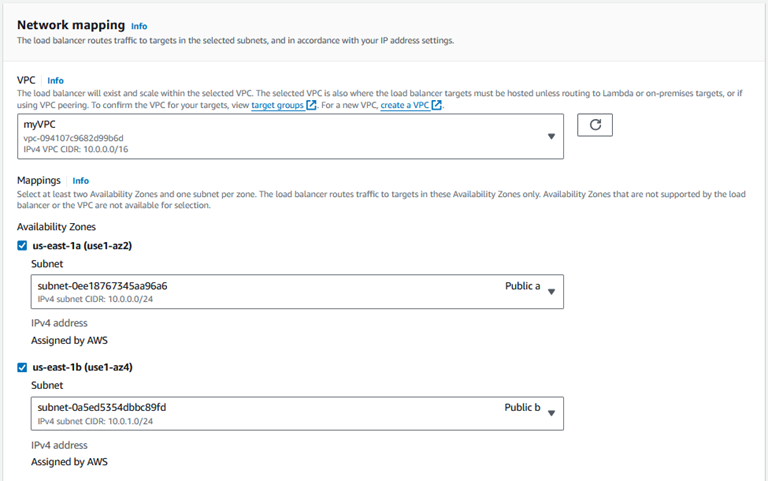
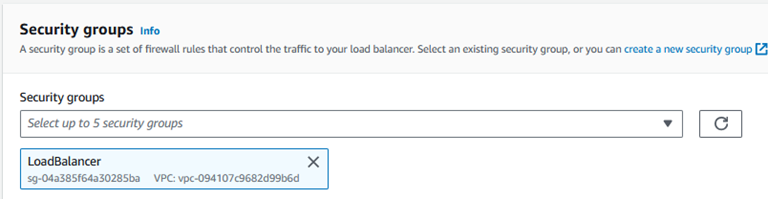
Choose your LoadBalancer security group we created previously.
Make sure your listener is using HTTPS : 443 and select the Target Group we created previously.
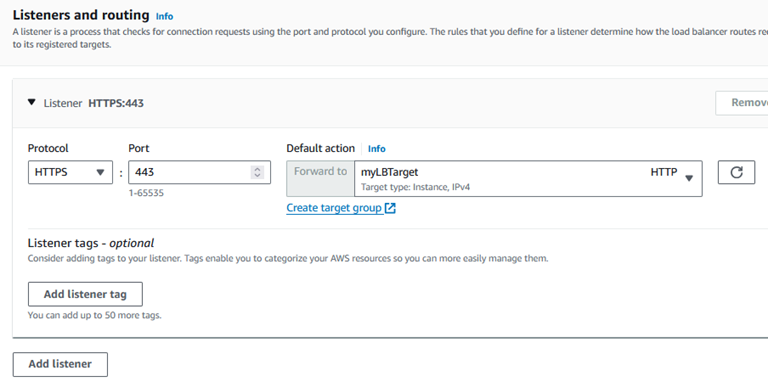
Select the “From ACM” for the server certificate and select your ACM certificate from earlier.
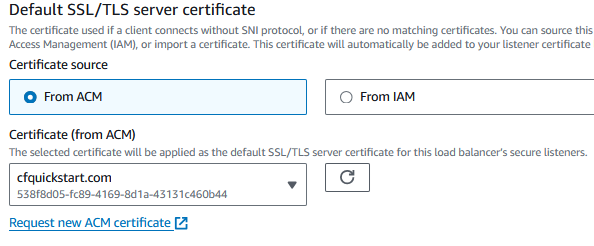
Check the “Include WAF security protections behind the load balancer”
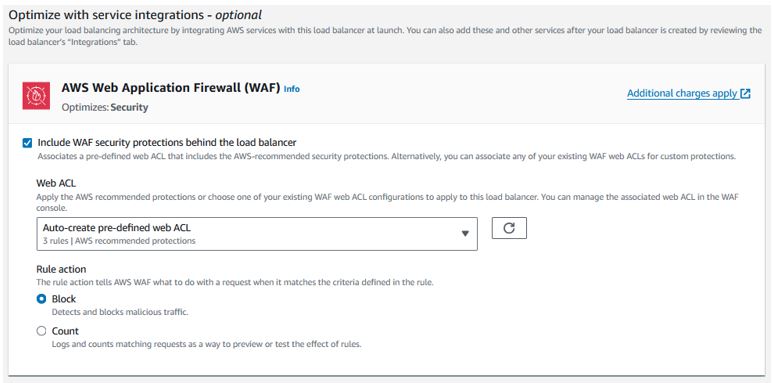
Click “Create load balancer”
DNS
Configure the DNS for ALB
Under Route 53 -> Hosted Zones, click on your hosted zone and click “Create record”Enter www (or whatever you want) into the subdomain, enable the Alias toggle, select the “Route traffic to” to be “Alias to Application and Classic Load Balancer”, choose your Region, and select your ALB from the dropdown menu.
Click “Create records”.
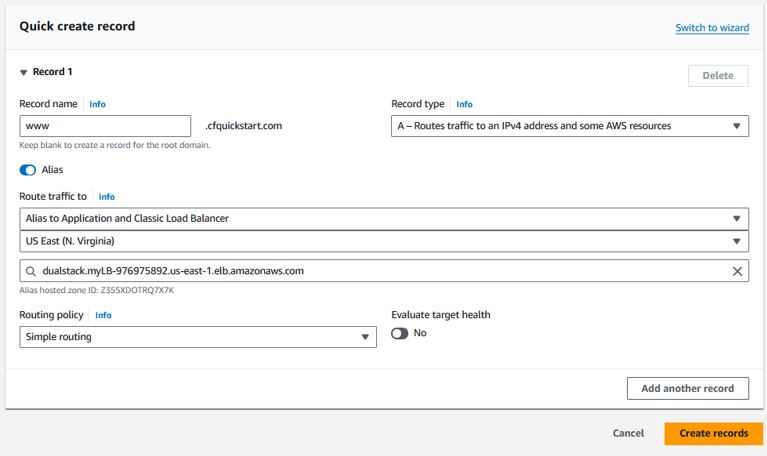
With a Route 53 alias, you can even point the domain apex (e.g. cfquickstart.com without any subdomain) to your load balancer. Normally this requires an IP address due to DNS standards.
Final Network Diagram
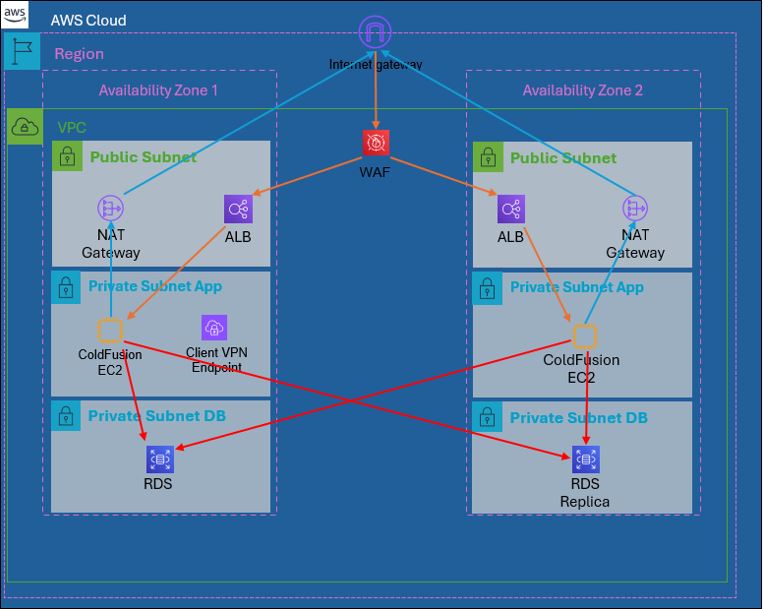
Administration
- Quotas
If you run into service limits as you start consuming more AWS services, you may be hitting a usage restriction that can be increased.
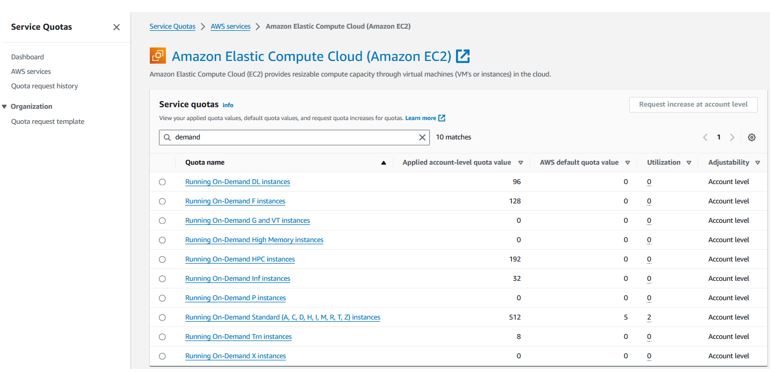
Visit “Service Quotas”
For example, drilling into the EC2 quotas and filtering for “demand”, we can see the vCPU usage we are Utilizing and how much we are limited. On this page, you can select and request an increase in your service limits if they are Adjustable.
- SSM Connection Demonstration
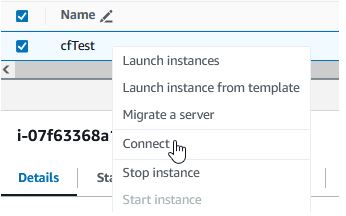
Under EC2 -> Instances. Click on your instance then click “Connect” (or right click and click “Connect”)
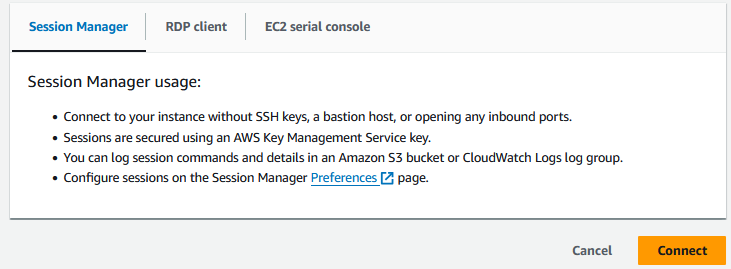
On the first tab (“Session Manager”), if you click Connect you will open a new browser window with access to the Powershell (Windows) or shell (Linux).
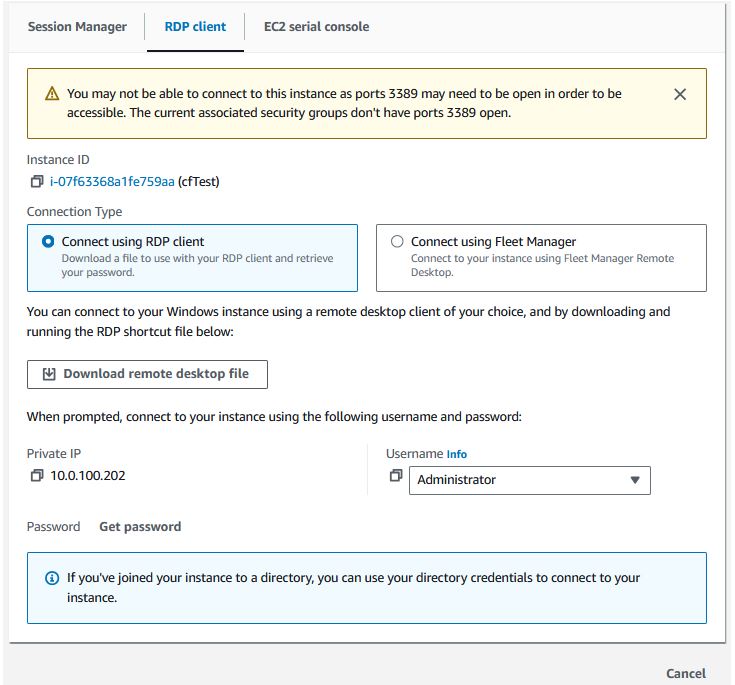
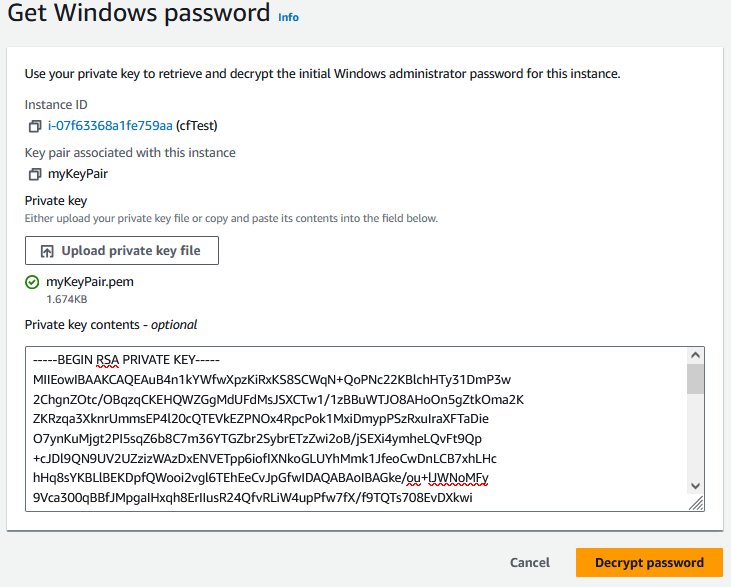
On the second tab shown (“RDP Client”), this is where you can retrieve the generated password for Windows.
You can click to download an RDP shortcut file that will assist you in opening an RDP connection to the server. If you click on “Get password”, you will be able to upload your KeyPair pem file that you downloaded earlier, and click “Decrypt password” to retrieve the password.
Alternatively, you can click on the “Connect using Fleet Manager” option, then you will be able to click “Fleet Manager Remote Desktop”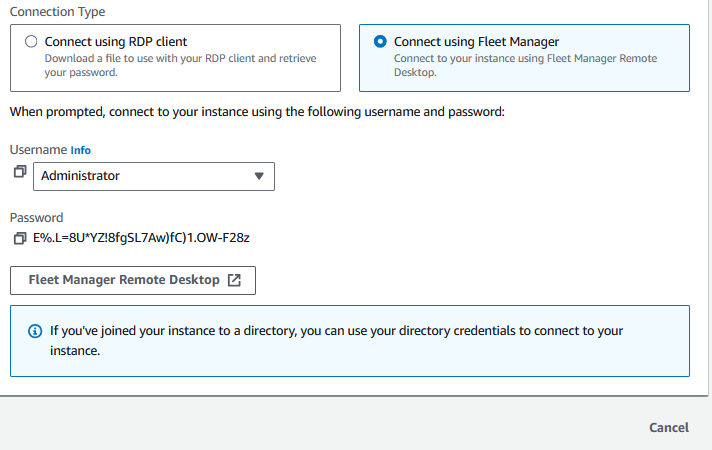
Then, you can select Authentication type “Key pair” and upload your PEM file and click “Connect”.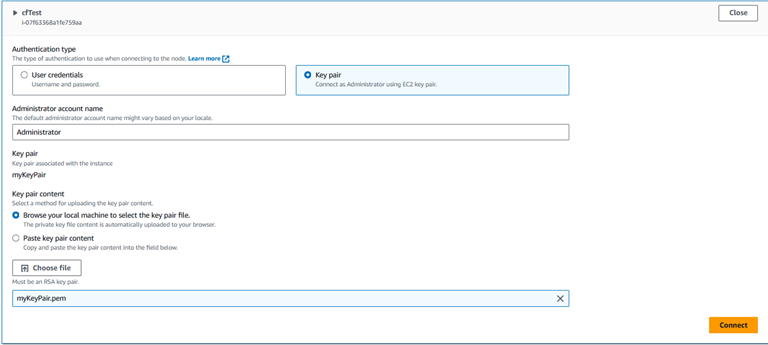
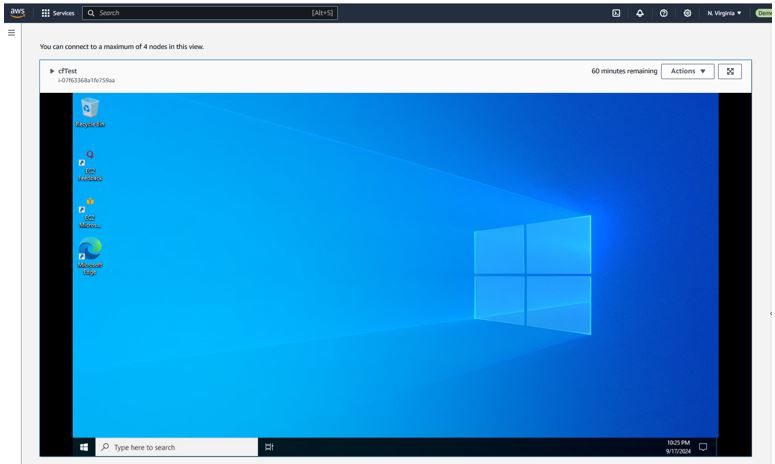
At this point, you connect to your server's desktop through your web browser:
- AWS Config
Visit AWS Config and either manually “Set up AWS Config” or click “1-click setup”. This will monitor your AWS resources and be able to log how configurations change over timerver's desktop through your web browser:
- GuardDuty
Visit GuardDuty and get started with all features to enable it. This uses ML to identify suspicious activity within your account and alert you accordingly.
- Detective
Visit Detective and click “Get started” to enable it. This collects log data from AWS resources and applies ML and other tools to help you investigate root causes of security issues or suspicious activities.
- Cloudwatch
Visit CloudWatch to view your logs, see your AWS service metrics, and set alarms.
- Security Hub
Visit Security Hub to configure automated security checks to identify and remediate security issues
Advanced Topics
Below are a sample of the advanced topics. List of other topics can be found on the agenda.- AWS Inspector
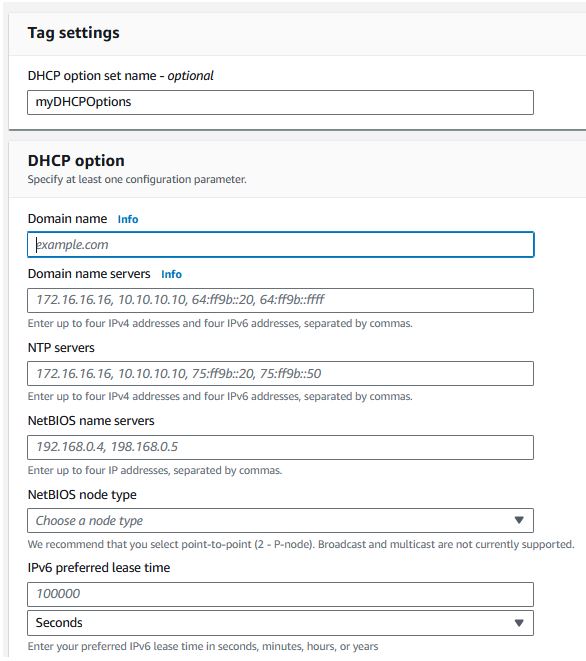
Vulnerability management by continually scanning your instances through agent or agentless methods. - DHCP Option Sets
Under VPC, you can create a custom DHCP Option Set to assign to your VPC. This lets you override various settings on resources running in your VPC, including the unqualified domain lookup value (e.g. a setting of company.local as the domain name means if you ping “theServerName”, it'll automatically look up DNS entry for theservername.company.local), the NTP (time sync servers), the DNS server, and more.
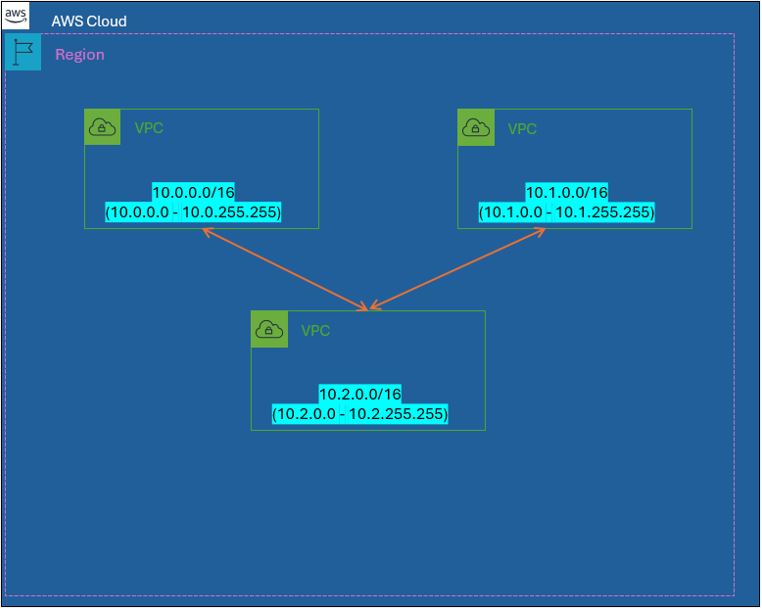
- VPC Peering
VPC Peering allows you to connect a pair of VPC's either within the same AWS Account or with an external AWS Account. Peering is free and charges only apply for data transfer for peerings that cross AZ's and Regions. CIDR blocks cannot overlap between VPCs and network traffic is not transitive (cannot hop across more than one peering connection).
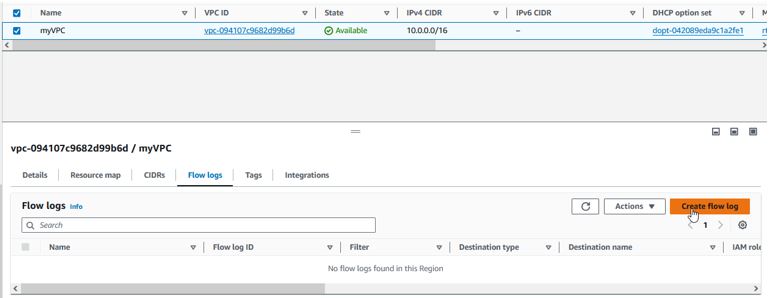
- VPC Flow Logs
Each VPC has the option to enable flow logs. This logs network packet communications handled by your VPC. VPC flow logs can generate a lot of log records, but it is a useful tool to understand traffic flow, server compromise traffic, and data exfiltration.
Glossary
- AWS Certificate Manager (ACM)
AWS Certificate Manager is a web service for provisioning, managing, and deploying Secure Sockets Layer/Transport Layer Security (SSL/TLS) certificates for use with AWS services. - Amazon Machine Image (AMI)
An Amazon Machine Image (AMI) is an encrypted machine image stored in Amazon EBS or Amazon S3. AMIs function similarly to a template of a computer's root drive. They contain the operating system and can also include software and layers of your application, such as database servers, middleware, and web servers. -
Amazon Resource Name (ARN)
Amazon Resource Name is a standardized way to refer to an AWS resource (for example, arn:aws:iam::123456789012:user/division_abc/subdivision_xyz/Bob). -
Aurora
Amazon Aurora is a fully managed MySQL-compatible relational database engine that combines the speed and availability of commercial databases with the simplicity and cost-effectiveness of open-source databases. -
Auto Scaling
AWS Auto Scaling is a fully managed service that you can use to quickly discover the scalable AWS resources that are part of your application and to configure dynamic scaling. -
Auto Scaling group (ASG)
A representation of multiple EC2 instances that share similar characteristics, and that are treated as a logical grouping for the purposes of instance scaling and management. -
Availability Zone (AZ)
A distinct location within a Region that's insulated from failures in other Availability Zones, and provides inexpensive, low-latency network connectivity to other Availability Zones in the same Region. -
Backup
AWS Backup is a managed backup service that you can use to centralize and automate the backup of data across AWS services in the cloud and on premises. -
Billing and Cost Management
AWS Billing and Cost Management is the AWS Cloud computing model where you pay for services on demand and use as much or as little as you need. While resources are active under your account, you pay for the cost of allocating those resources. You also pay for any incidental usage associated with those resources, such as data transfer or allocated storage. -
CIDR block
Classless Inter-Domain Routing. An internet protocol address allocation and route aggregation methodology. -
CloudFormation
AWS CloudFormation is a service for writing or changing templates that create and delete related AWS resources together as a unit. -
CloudFront
Amazon CloudFront is an AWS content delivery service that helps you improve the performance, reliability, and availability of your websites and applications. -
CloudTrail
AWS CloudTrail is a web service that records AWS API calls for your account and delivers log files to you. The recorded information includes the identity of the API caller, the time of the API call, the source IP address of the API caller, the request parameters, and the response elements that the AWS service returns. -
CloudWatch
Amazon CloudWatch is a web service that you can use to monitor and manage various metrics, and configure alarm actions based on data from those metrics. -
CloudWatch Logs
Amazon CloudWatch Logs is a web service for monitoring and troubleshooting your systems and applications from your existing system, application, and custom log files. You can send your existing log files to CloudWatch Logs and monitor these logs in near-real time. -
Command Line Interface (CLI)
AWS Command Line Interface is a unified downloadable and configurable tool for managing AWS services. Control multiple AWS services from the command line and automate them through scripts. -
Config
AWS Config is a fully managed service that provides an AWS resource inventory, configuration history, and configuration change notifications for better security and governance. You can create rules that automatically check the configuration of AWS resources that AWS Config records. -
Control Tower
AWS Control Tower is a service used to set up and govern a secure, multi-account AWS environment. -
DB parameter group
A container for database engine parameter values that apply to one or more DB instances. -
Detective
Amazon Detective is a service that collects log data from your AWS resources to analyze and identify the root cause of security findings or suspicious activities. The Detective behavior graph provides visualizations to help you to determine the nature and extent of possible security issues and conduct an efficient investigation. -
Directory Service
AWS Directory Service is a managed service for connecting your AWS resources to an existing on-premises Microsoft Active Directory or to set up and operate a new, standalone directory in the AWS Cloud. -
Database Migration Service (DMS)
AWS Database Migration Service is a web service that can help you migrate data to and from many widely used commercial and open-source databases. -
Elastic Block Store (EBS)
Amazon Elastic Block Store is a service that provides block level storage volumes or use with EC2 instances. -
Elastic Load Balancing (ELB)
Elastic Load Balancing is a web service that improves an application's availability by distributing incoming traffic between two or more EC2 instances. There are four types of ELB services – Classic Load Balancer, Application Load Balancer (ALB), Network Load Balancer (NLB), and Gateway Load Balancer (GLB). -
Elastic Compute Cloud (EC2)
Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud is a web service for launching and managing Linux/UNIX and Windows Server instances in Amazon data centers. -
Elastic IP address (EIP)
A fixed (static) IP address that you have allocated in Amazon EC2 or Amazon VPC and then attached to an instance. Elastic IP addresses are associated with your account, not a specific instance. They are elastic because you can easily allocate, attach, detach, and free them as your needs change. Unlike traditional static IP addresses, Elastic IP addresses allow you to mask instance or Availability Zone failures by rapidly remapping your public IP addresses to another instance. -
Elastic Network Interface (ENI)
An elastic network interface is additional network interface that can be attached to an instance. Elastic network interfaces include a primary private IP address, one or more secondary private IP addresses, an Elastic IP Address (optional), a MAC address, membership in specified security groups, a description, and a source/destination check flag. You can create an elastic network interface, attach it to an instance, detach it from an instance, and attach it to another instance. -
ElastiCache
Amazon ElastiCache is a web service that simplifies deploying, operating, and scaling an in-memory cache in the cloud (Redis, Memcached). The service improves the performance of web applications by providing information retrieval from fast, managed, in-memory caches, instead of relying entirely on slower disk-based databases. -
EventBridge
Amazon EventBridge is a serverless event bus service that you can use to connect your applications with data from a variety of sources and routes that data to targets such as AWS Lambda. You can set up routing rules to determine where to send your data to build application architectures that react in real time to all of your data sources. -
GovCloud
AWS GovCloud (US) is an isolated AWS Region that hosts sensitive workloads in the cloud, ensuring that this work meets the US government's regulatory and compliance requirements. The AWS GovCloud (US) Region adheres to United States International Traffic in Arms Regulations (ITAR), Federal Risk and Authorization Management Program (FedRAMP) requirements, Department of Defense (DOD) Cloud Security Requirements Guide (SRG) Levels 2 and 4, and Criminal Justice Information Services (CJIS) Security Policy requirements. -
GuardDuty
Amazon GuardDuty is a continuous security monitoring service. Amazon GuardDuty can help to identify unexpected and potentially unauthorized or malicious activity in your AWS environment. -
Identity and Access Management (IAM)
AWS Identity and Access Management is a web service that Amazon Web Services (AWS) customers can use to manage users and user permissions within AWS. -
IAM Identity Center
AWS IAM Identity Center is a cloud-based service that brings together administration of users and their access to AWS accounts and cloud applications. You can control single sign-on access and user permissions across all your AWS accounts in AWS Organizations. -
Instance Type
A specification that defines the memory, CPU, storage capacity, and usage cost for an instance. Some instance types are for standard applications, whereas others are for CPU-intensive, memory-intensive applications. -
Internet Gateway
Connects a network to the internet. You can route traffic for IP addresses outside your Amazon VPC to the internet gateway. -
Key Management Service (KMS)
AWS Key Management Service is a managed service that simplifies the creation and control of encryption keys that are used to encrypt data. -
Key Pair
A set of security credentials that you use to prove your identity electronically. A key pair consists of a private key and a public key. -
AWS Management Console
AWS Management Console is a graphical interface to manage compute, storage, and other cloud resources. -
AWS Marketplace
AWS Marketplace is a web portal where qualified partners market and sell their software to AWS customers. AWS Marketplace is an online software store that helps customers find, buy, and immediately start using the software and services that run on AWS. -
Multi-AZ deployment
A primary DB instance that has a synchronous standby replica in a different Availability Zone. The primary DB instance is synchronously replicated across Availability Zones to the standby replica. -
Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
An optional AWS account security feature. After you enable AWS MFA, you must provide a six-digit, single-use code in addition to your sign-in credentials whenever you access secure AWS webpages or the AWS Management Console. You get this single-use code from an authentication device that you keep in your physical possession. -
NAT gateway
A Network Address Translation (NAT) device, managed by AWS, that performs network address translation in a private subnet, to secure inbound internet traffic. A NAT gateway uses both NAT and port address translation. -
Network ACL
An optional layer of security that acts as a firewall for controlling traffic in and out of a subnet. You can associate multiple subnets with a single network ACL, but a subnet can be associated with only one network ACL at a time. -
Organizations
AWS Organizations is an account management service that you can use to consolidate multiple AWS accounts into an organization that you create and centrally manage. -
Relational Database Service (RDS)
Amazon Relational Database Service is a web service that makes it easier to set up, operate, and scale a relational database in the cloud. It provides cost-efficient, resizable capacity for an industry-standard relational database and manages common database administration tasks. -
Redis
A fast, open-source, in-memory key-value data structure store. Redis comes with a set of versatile in-memory data structures with which you can easily create a variety of custom applications. -
Region
A named set of AWS resources that's in the same geographical area. A Region is comprised of at least three Availability Zones. AWS Regions are divided into partitions. AWS commercial Regions are in the AWS partition, China Regions are in the AWS-cn partition, and AWS GovCloud (US) Regions are in the AWS-us-gov partition. -
Reserved Instance
A pricing option for EC2 instances that discounts the on-demand usage charge for instances that meet the specified parameters. Customers pay for the entire term of the instance, regardless of how they use it. -
Route 53
Amazon Route 53 is a web service that you can use to create a new DNS service or to migrate your existing DNS service to the cloud. -
Route Table
A set of routing rules that controls the traffic leaving any subnet that's associated with the route table. You can associate multiple subnets with a single route table, but a subnet can be associated with only one route table at a time. -
Simple Storage Service (S3)
Amazon S3 is storage for the internet. You can use it to store and retrieve any amount of data at any time, from anywhere on the web. -
Security Group
A named set of allowed inbound network connections for an instance. (Security groups in Amazon VPC also include support for outbound connections.) Each security group consists of a list of protocols, ports, and IP address ranges. A security group can apply to multiple instances, and multiple groups can regulate a single instance. -
Security Hub
AWS Security Hub is a service that provides a comprehensive view of the security state of your AWS resources. Security Hub collects security data from AWS accounts and services and helps you analyze your security trends to identify and prioritize the security issues across your AWS environment. -
Service Quotas
A service for viewing and managing your quotas easily and at scale as your AWS workloads grow. Quotas, also referred to as limits, are the maximum number of resources that you can create in an AWS account. -
Service Role
An IAM role that grants permissions to an AWS service so it can access AWS resources. The policies that you attach to the service role determine which AWS resources the service can access and what it can do with those resources. -
Simple Email Service (SES)
Amazon Simple Email Service is a simple and cost-effective email solution for applications. -
Shield
AWS Shield is a service that helps to protect your resources—such as Amazon EC2 instances, Elastic Load Balancing load balancers, Amazon CloudFront distributions, and Route 53 hosted zones—against DDoS attacks. AWS Shield is automatically included at no extra cost beyond what you already pay for AWS WAF and your other AWS services. For added protection against DDoS attacks, AWS offers AWS Shield Advanced. -
Simple Notification Service (SNS)
Amazon Simple Notification Service is a web service that applications, users, and devices can use to instantly send and receive notifications from the cloud. -
Systems Manager (SSM)
AWS Systems Manager is the operations hub for AWS and hybrid cloud environments that can help achieve secure operations at scale. It provides a unified user interface for users to view operations data from multiple AWS services and automate tasks across their AWS resources. -
Trusted Advisor
AWS Trusted Advisor is a web service that inspects your AWS environment and makes recommendations for saving money, improving system availability and performance, and helping to close security gaps. -
Virtual Private Cloud (VPC)
Amazon Virtual Private Cloud is a web service for provisioning a logically isolated section of the AWS Cloud virtual network that you define. You control your virtual networking environment by selecting your own IP address range, creating subnets and configuring route tables and network gateways. -
VPC endpoint
A feature that you can use to create a private connection between your Amazon VPC and another AWS service without requiring access over the internet, through a NAT instance, a VPN connection, or Direct Connect. -
Virtual Private Network (VPN)
AWS Virtual Private Network provides functionality that establishes encrypted connections between your network or device, and AWS. AWS VPN is comprised of two services: AWS Client VPN and AWS Site-to-Site VPN. -
Web Application Firewall (WAF)
AWS WAF is a web application firewall service that controls access to content by allowing or blocking web requests based on criteria that you specify. For example, you can filter access based on the header values or the IP addresses that the requests originate from. AWS WAF helps protect web applications from common web exploits that could affect application availability, compromise security, or consume excessive resources. -
WorkSpaces
Amazon WorkSpaces is a managed, secure desktop computing service for provisioning cloud-based desktops and providing users access to documents, applications, and resources from supported devices.